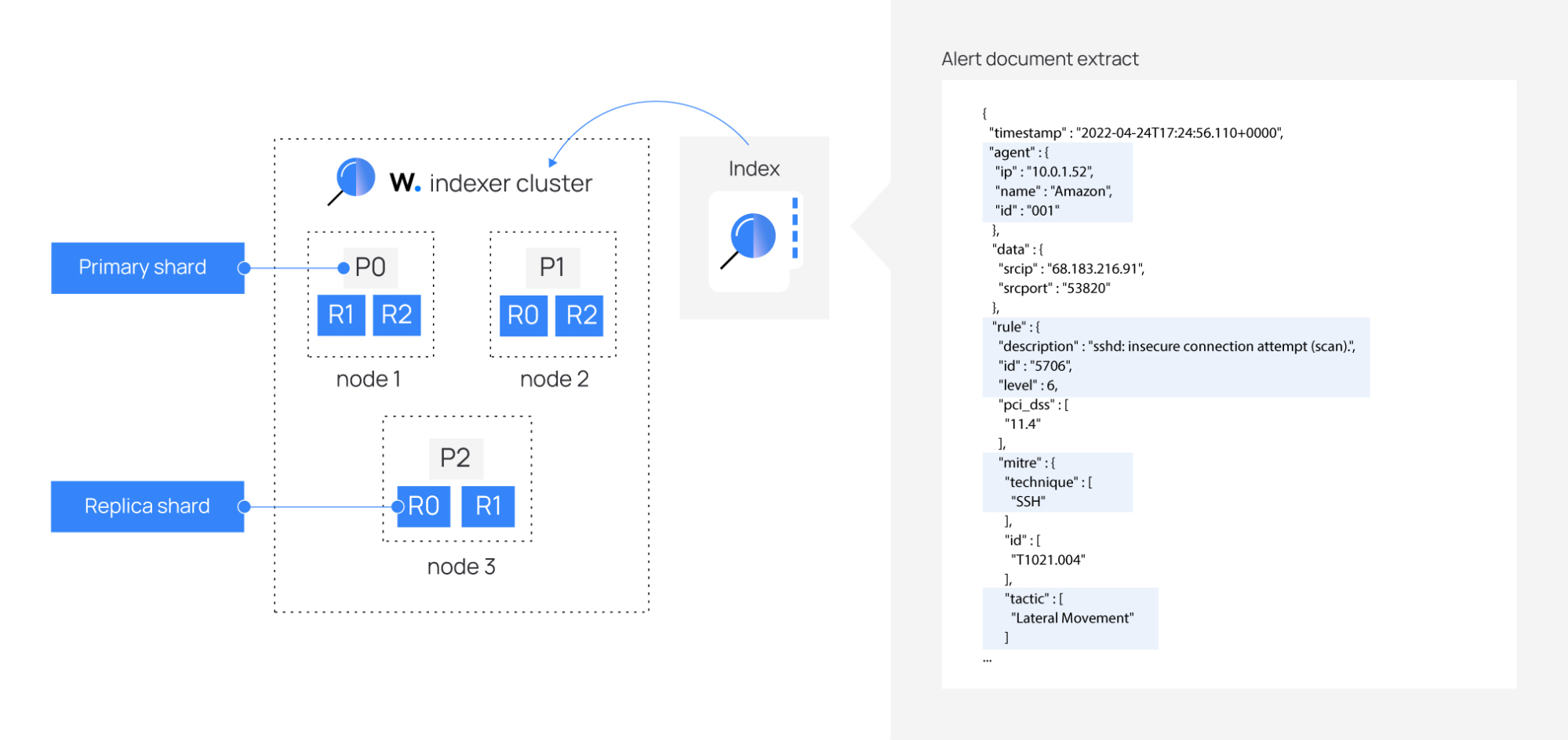
Wazuh indexer tuning
This guide shows how to change settings to optimize the Wazuh indexer performance. To change the Wazuh indexer password, see the Password management section.
Memory locking
When the system is swapping memory, the Wazuh indexer may not work as expected. Therefore, it is important for the health of the Wazuh indexer node that none of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) is ever swapped out to disk. To prevent any Wazuh indexer memory from being swapped out, configure the Wazuh indexer to lock the process address space into RAM as follows.
Note
You require root user privileges to run the commands described below.
Add the below line to the
/etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.ymlconfiguration file on the Wazuh indexer to enable memory locking:bootstrap.memory_lock: true
Modify the limit of system resources. Configuring system settings depends on the operating system of the Wazuh indexer installation.
Create a new directory for the file that specifies the system limits:
# mkdir -p /etc/systemd/system/wazuh-indexer.service.d/
Run the following command to create the
wazuh-indexer.conffile in the newly created directory with the new system limit added:# cat > /etc/systemd/system/wazuh-indexer.service.d/wazuh-indexer.conf << EOF [Service] LimitMEMLOCK=infinity EOF
Create a new directory for the file that specifies the system limits:
# mkdir -p /etc/init.d/wazuh-indexer.service.d/
Run the following command to create the
wazuh-indexer.conffile in the newly created directory with the new system limit added:# cat > /etc/init.d/wazuh-indexer.service.d/wazuh-indexer.conf << EOF [Service] LimitMEMLOCK=infinity EOF
Edit the
/etc/wazuh-indexer/jvm.optionsfile and change the JVM flags. Set a Wazuh indexer heap size value to limit memory usage. JVM heap limits prevent theOutOfMemoryexception if the Wazuh indexer tries to allocate more memory than is available due to the configuration in the previous step. The recommended value is half of the system RAM. For example, set the size as follows for a system with 8 GB of RAM.-Xms4g -Xmx4g
Where the total heap space:
-Xms4g- initial size is set to 4Gb of RAM.-Xmx4g- maximum size is to 4Gb of RAM.
Warning
To prevent performance degradation due to JVM heap resizing at runtime, the minimum (Xms) and maximum (Xmx) size values must be the same.
Restart the Wazuh indexer service:
# systemctl daemon-reload # systemctl restart wazuh-indexer
Verify that the setting was changed successfully, by running the following command to check that
mlockallvalue is set totrue:# curl -k -u <INDEXER_USERNAME>:<INDEXER_PASSWORD> "https://<INDEXER_IP_ADDRESS>:9200/_nodes?filter_path=**.mlockall&pretty"
{ "nodes" : { "sRuGbIQRRfC54wzwIHjJWQ" : { "process" : { "mlockall" : true } } } }
If the output is
false, the request has failed, and the following line appears in the/var/log/wazuh-indexer/wazuh-indexer.logfile:Unable to lock JVM Memory
Configure shard allocation awareness or forced awareness
This is most applicable in cases where the Wazuh indexer nodes are spread across geographically dispersed zones.
To configure awareness, add zone attributes to the /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.yml file on the Wazuh indexer nodes for the different zones.
For example: You have two zones named zone A and B. You will add the following configuration to the /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.yml file on each Wazuh indexer node in zone A and B respectively:
node.attr.zone: zoneA
node.attr.zone: zoneB
Allocation awareness is best used if storage on the Wazuh indexer nodes in zone A and zone B is less than 50% utilized. This allows for adequate storage capacity to allocate replicas in the zone.
Forced awareness is an option if Wazuh indexer nodes in both zone A and B lack sufficient capacity to store all primary and replica shards. This ensures that if there's a zone failure, the Wazuh indexer won't overwhelm your remaining zone, preventing your cluster from being locked due to storage shortage.
Choosing allocation awareness or forced awareness depends on how much space you have in each zone to balance your primary and replica shards.
Forced awareness
Using the forced awareness implies that primary and replica shards are never allocated to the same zone.
To configure forced awareness, specify all the possible values for your zone attributes:
PUT _cluster/settings
{
"persistent": {
"cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.attributes": "zone",
"cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.force.zone.values":["zoneA", "zoneB"]
}
}
In case there are other zones, add the other zones to the cluster.routing.allocation.awareness.force.zone.values field.
Warning
If a node fails, forced awareness does not allocate the replicas to another node in the same zone. Instead, the cluster enters a yellow state and only allocates the replicas when nodes in the other zone(s) come online.
Allocation filtering
This allows a node to be excluded from shard allocation. A common use case is when you want to decommission a node within a zone.
To move shards off a node before decommissioning it, create a filter that excludes the node using its IP address. This will move all shards allocated to that node before it is shut down. You can also use a wildcard * in a situation where there are more than one node within an IP range to be decommissioned.
PUT _cluster/settings
{
"persistent": {
"cluster.routing.allocation.exclude._ip": "192.168.0.*"
}
}
Set node attributes for each node in a cluster
By default, each Wazuh indexer node is a master-eligible, data, ingest, and coordinating node. Deciding on the number of nodes, assigning node types, and choosing the hardware for each node type depends on your use case.
Cluster manager nodes
Cluster manager nodes manage all cluster-wide configurations and modifications, including adding, removing, and allocating shards to nodes, as well as generating and deleting indices and fields.
A distributed consensus technique is used to elect a single cluster-manager node from among the cluster-manager eligible nodes. This cluster-manager node is reelected in the event that the incumbent node fails.
You can specify that a Wazuh indexer node is the cluster manager node, even though this is already done by default.
Set a Wazuh indexer node role to cluster_manager by adding the following configuration to the /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.yml file:
node.roles: [ cluster_manager ]
Data nodes
The data node is responsible for storing and searching data. It performs all data related operations (indexing, searching, aggregating) on local shards. These are the worker nodes of your Wazuh indexer cluster and need more disk space than any other node type.
Set a Wazuh indexer node role as a data node by adding the following configuration to the /etc/wazuh-indexer/opensearch.yml file:
node.roles: [ data, ingest ]
As you add data nodes it is important to keep them balanced between zones. For example, if you have three zones, add a data node for each zone. We recommend using storage and RAM-heavy nodes.
Coordinating nodes
The coordinating node delegates client requests to the shards on the data nodes, collects and aggregates the results into one final result, and sends it back to the Wazuh dashboard.
Every node is a coordinating node by default, however to make a node a dedicated coordinating node, set node.roles to an empty list:
node.roles: []