Configuration
Basic usage
Log data collection is configured in the ossec.conf file primarily in the localfile, remote and global sections. Configuration of log data collection can also be completed in the agent.conf file to centralize the distribution of these configuration settings to relevant agents.
As in this basic usage example, provide the name of the file to be monitored and the format:
<localfile>
<location>/var/log/messages</location>
<log_format>syslog</log_format>
</localfile>
Monitoring logs using regular expressions for file names
Wazuh supports posix regular expressions. For example, to analyze every file that ends with a .log inside the /var/log directory, use the following configuration:
<localfile>
<location>/var/log/*.log</location>
<log_format>syslog</log_format>
</localfile>
Monitoring date-based logs
For log files that change according to the date, you can also specify a strftime format to replace the day, month, year, etc. For example, to monitor the log files like C:\Windows\app\log-08-12-15.log, where 08 is the year, 12 is the month and 15 the day (and it is rolled over every day), configuration is as follows:
<localfile>
<location>C:\Windows\app\log-%y-%m-%d.log</location>
<log_format>syslog</log_format>
</localfile>
Reading logs from Windows Event Log
To monitor a Windows event log, you need to provide the format as "eventlog" and the location as the name of the event log:
<localfile>
<location>Security</location>
<log_format>eventlog</log_format>
</localfile>
Reading events from Windows Event Channel
You can additionally monitor specific Windows event channels. The location is the name of the event channel. This is the only way to monitor the Applications and Services logs. If the file name contains a "%", replace it with "/":
<localfile>
<location>Microsoft-Windows-PrintService/Operational</location>
<log_format>eventchannel</log_format>
</localfile>
The eventchannel log format has been enhanced for Wazuh v3.8.0 with a new event data processing, keeping the old functionality and configuration. It allows to monitor every event generated at any Windows agent, returning every channel’s information in JSON format. As the old eventchannel, with this log_format the channels can be queried, filtering by event ID, process, logon type, or any other field contained in the generated event, giving the possibility to retrieve only the desired events.
This new option uses the JSON decoder to draw the event fields, ensuring a new way to add rules easier than before. The default channels included at the Wazuh ruleset are Application, Security, System, Microsoft-Windows-Sysmon/Operational, Microsoft Antimalware (Microsoft Security Essentials), Microsoft-Windows-Windows Defender/Operational and Microsoft-Windows-Eventlog.
Some sample events from Windows eventchannel are shown in the next images:
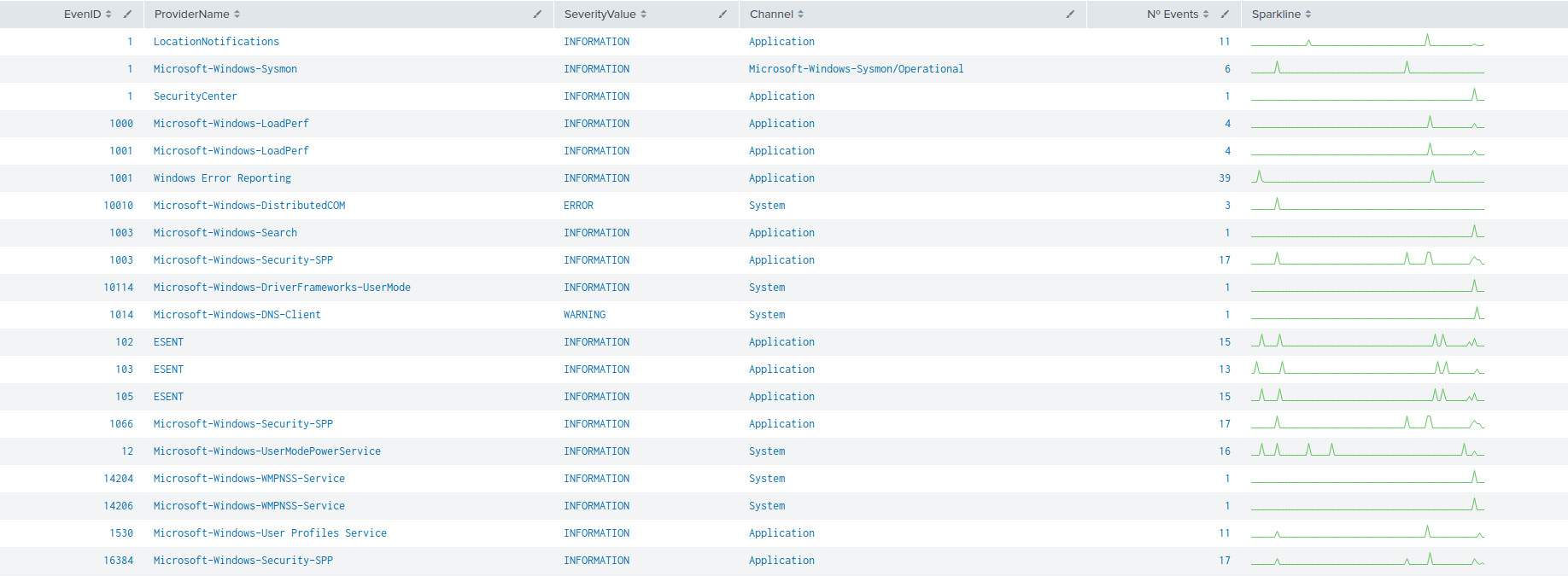
The following image represents the number of events of each channel, filtered by provider name along the time.
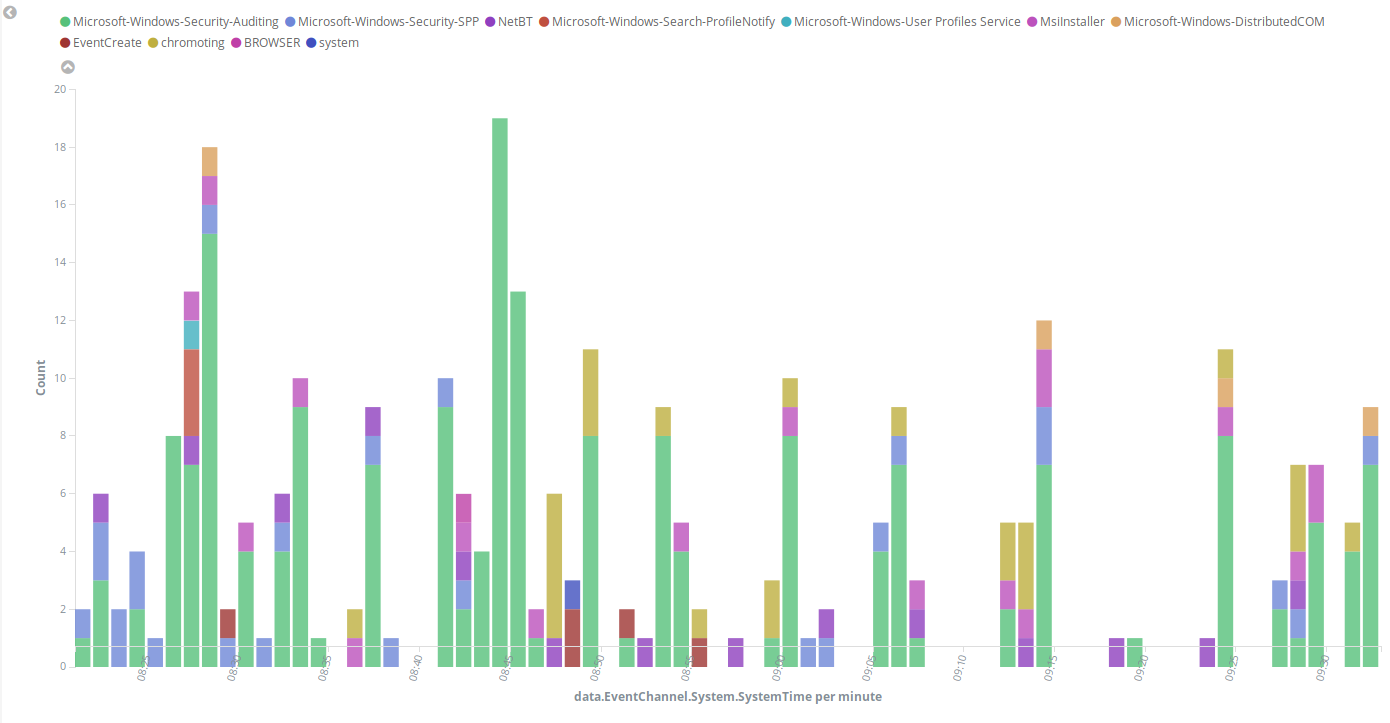
Filtering events from Windows Event Channel with queries
Events from the Windows Event channel can be filtered as below:
<localfile>
<location>System</location>
<log_format>eventchannel</log_format>
<query>Event/System[EventID=7040]</query>
</localfile>
Using environment variables
Environment variables like %WinDir% can be used in the location pattern. The following is an example of reading logs from an IIS server:
<localfile>
<location>%WinDir%\System32\LogFiles\W3SVC3\ex%y%m%d.log</location>
<log_format>iis</log_format>
</localfile>
Using multiple outputs
Log data is sent to the agent socket by default, but it is also possible to specify other sockets as output. ossec-logcollector uses UNIX type sockets to communicate allowing TCP or UDP protocols.
To add a new output socket we need to specify it using the tag <socket> as shown in the following example configuration:
<socket>
<name>custom_socket</name>
<location>/var/run/custom.sock</location>
<mode>tcp</mode>
<prefix>custom_syslog: </prefix>
</socket>
<socket>
<name>test_socket</name>
<location>/var/run/test.sock</location>
</socket>
Note
More information about defining a socket: socket
Once the socket is defined, it's possible to add the destination socket for each localfile:
<localfile>
<log_format>syslog</log_format>
<location>/var/log/messages</location>
<target>agent,test_socket</target>
</localfile>
<localfile>
<log_format>syslog</log_format>
<location>/var/log/messages</location>
<target>custom_socket,test_socket</target>
</localfile>
Warning
To keep the output to the default socket we need to specify it using 'agent' as target. Otherwise the output will be redirected only to the specified targets.