Monitoring Services
Azure Active Directory is the identity and directory management service that combines basic directory services, application access management, and identity protection in a single solution.
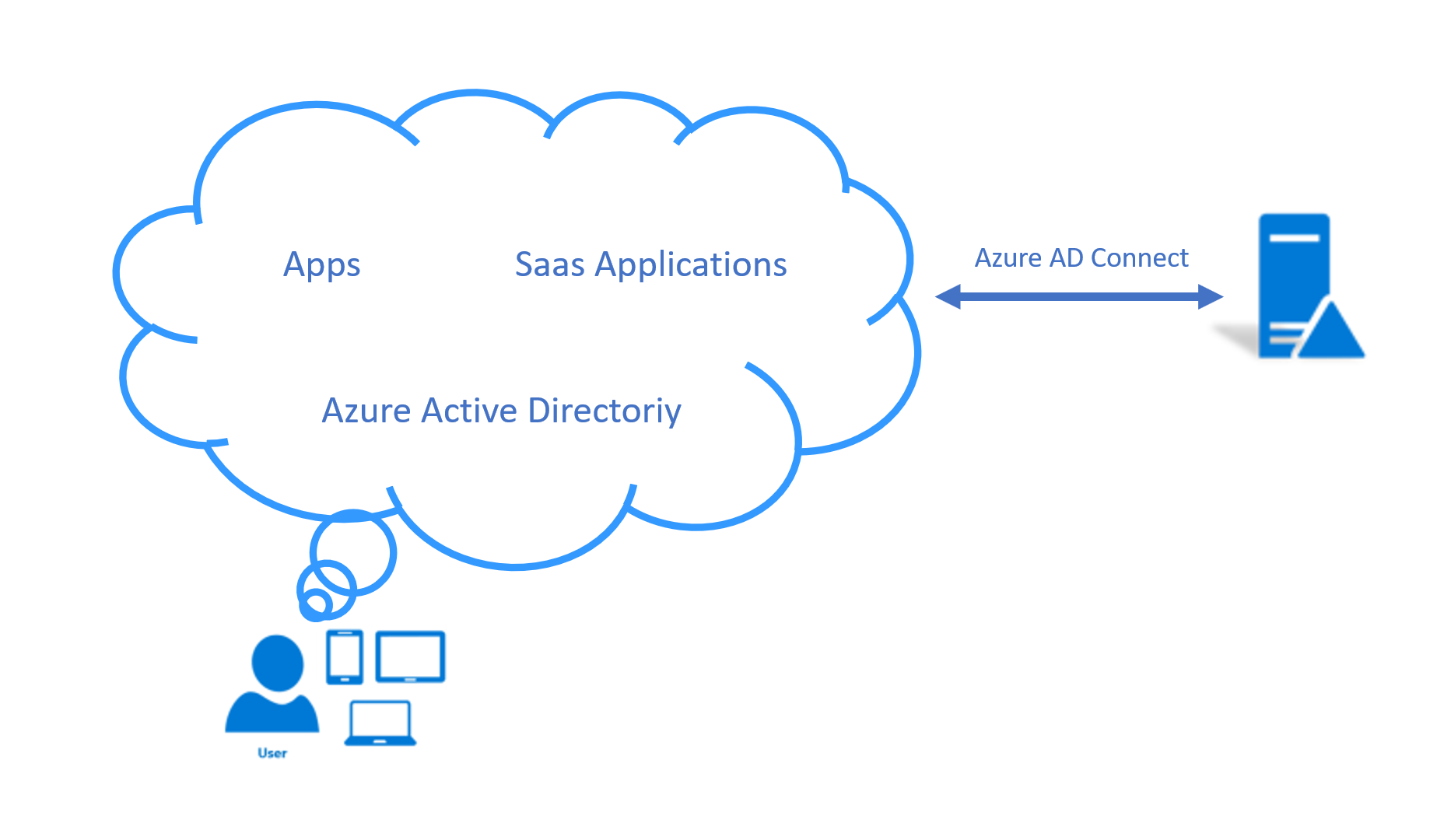
Wazuh also allows to monitor services such as Azure Active Directory using the Azure Active Directory Graph REST API, which provides access to Azure AD through REST API endpoints. Applications can use the Azure AD Graph API to perform read operations on directory data and objects.
Using Azure Active Directory Graph
We're going to configure an application from the Microsoft Azure portal to be able to use the Azure Active Directory Graph REST API.
Note
The process explained below details the configuration of an application that will use the Active Directory Graph REST API. You can also create a new application, as the creation process is similar to the application for Azure Log Analytics.
1. Giving permissions to the application
1.1 - In the Azure Active Directory section, select the option App registrations and once inside, select New application registration.
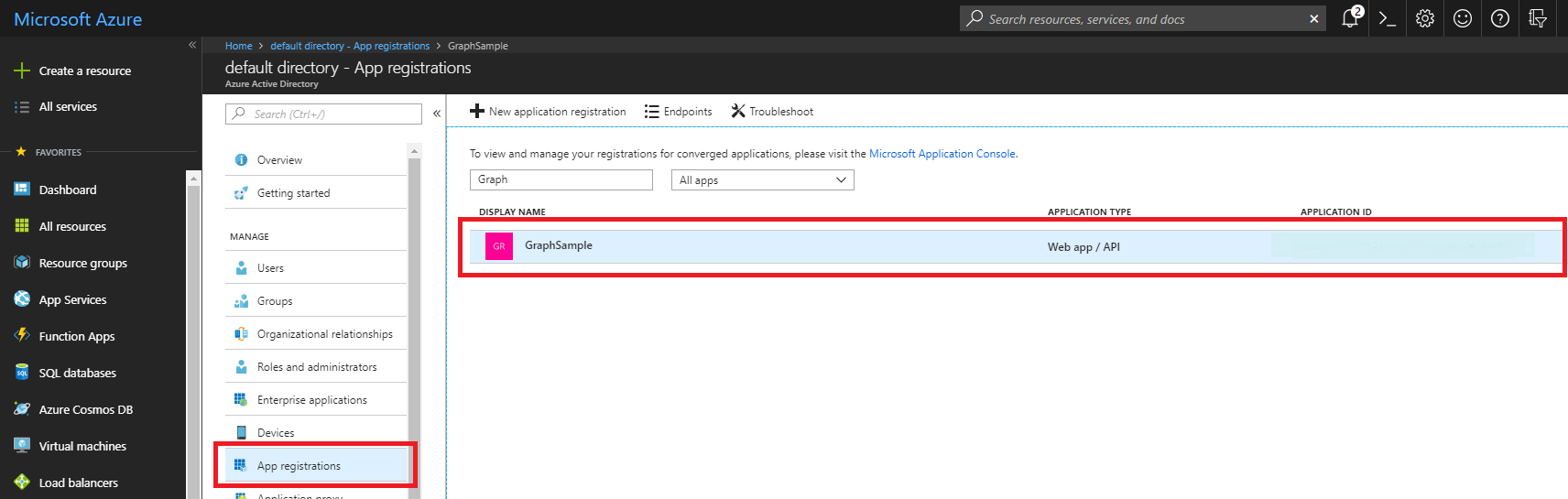
1.2 - Access the Settings section. Save the application id for later authentication.
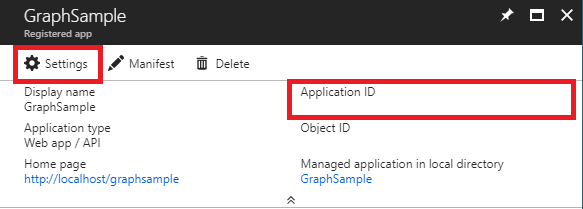
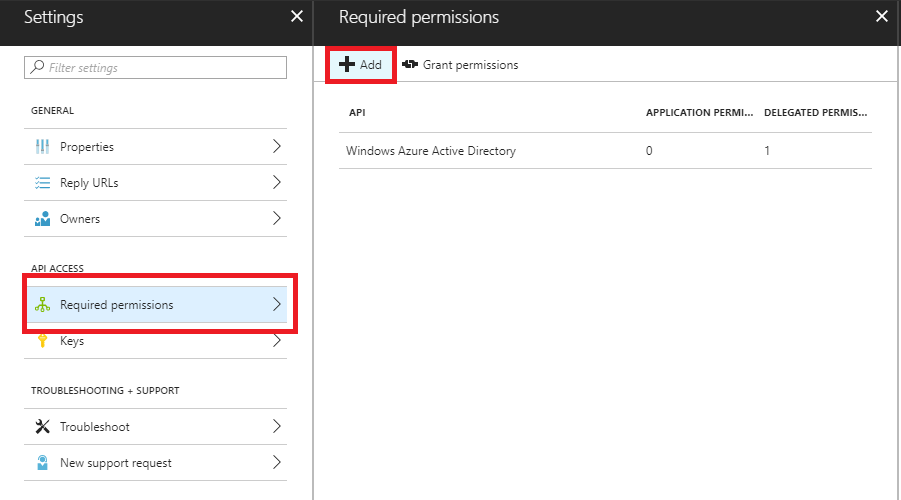
1.3 - In the Required permissions section select the Add option.
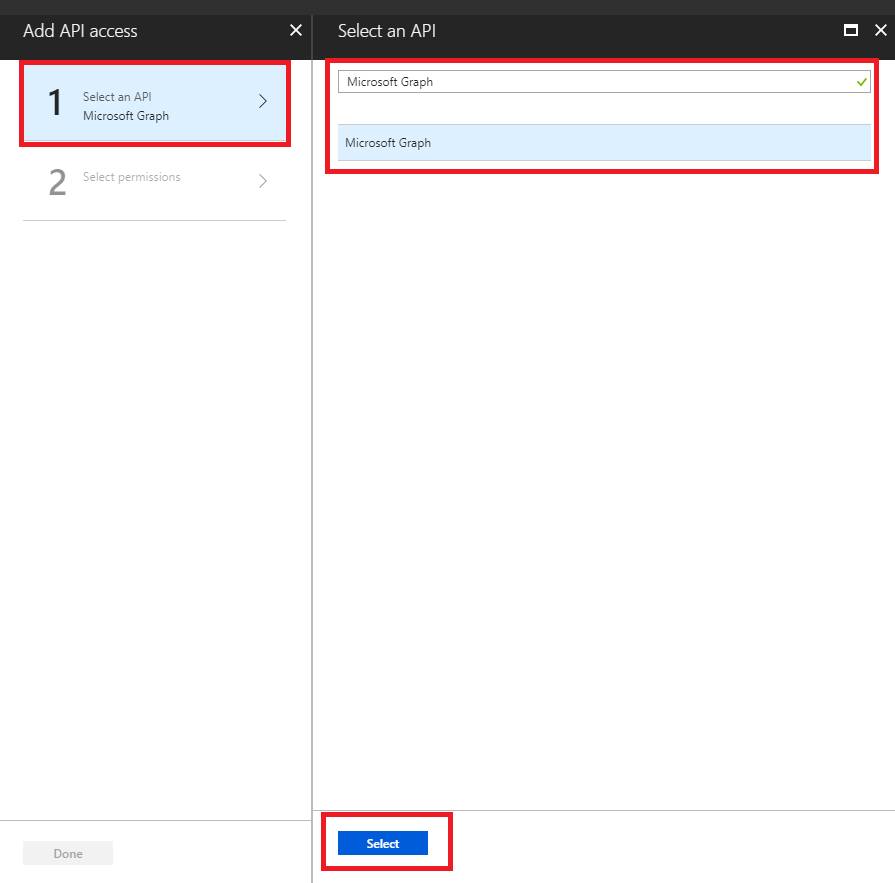
1.4 - Select the API by searching for "Microsoft Graph".
1.5 - Select the permissions that adapt to our infrastructure.
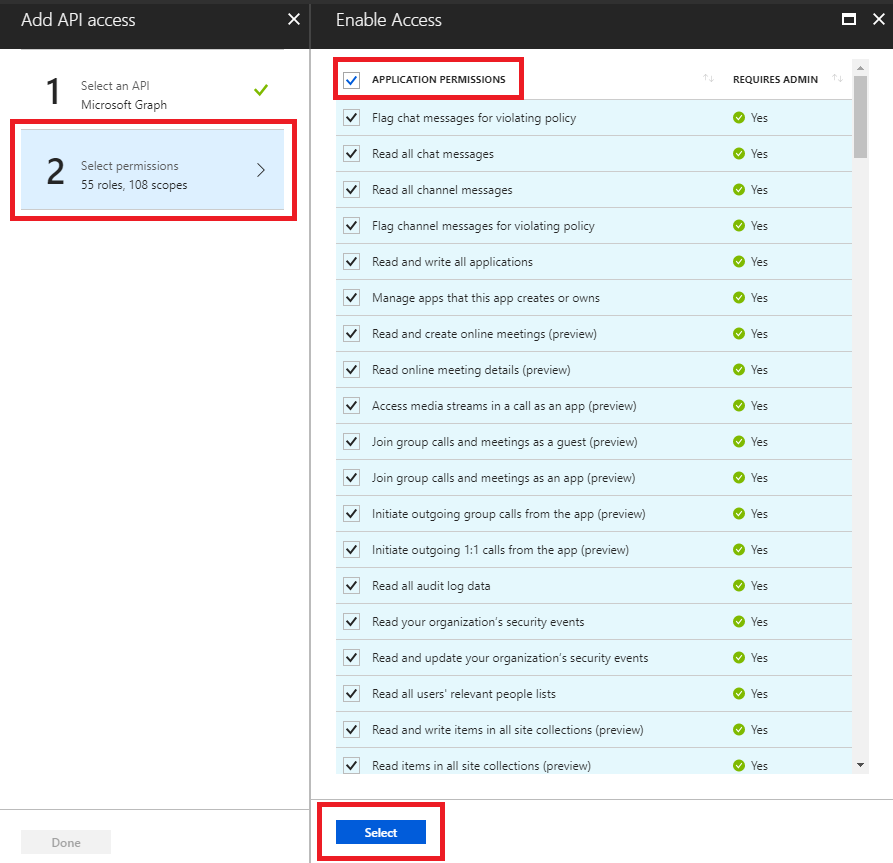
1.6 - Select Done.
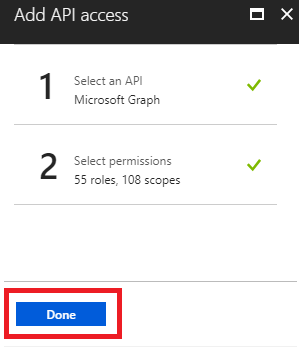
1.7 - Back to the Azure Active Directory section, select the option Enterprise applications and once inside, select the newly created app. Open Permissions and click Grant Admin Consent for the application. In the popup window that appears, review the permissions are appropriate, and select Accept.
2. Obtaining the application key for authentication
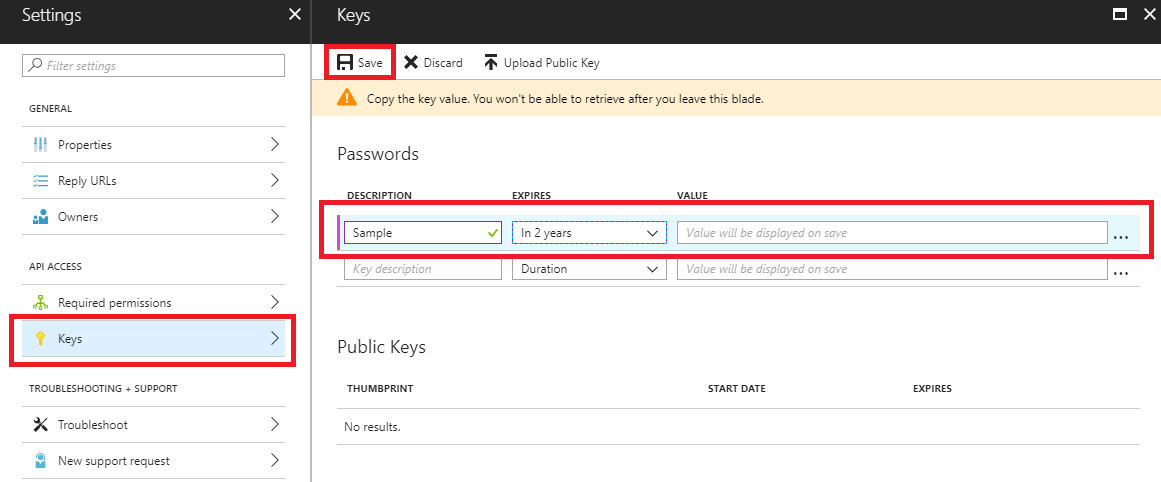
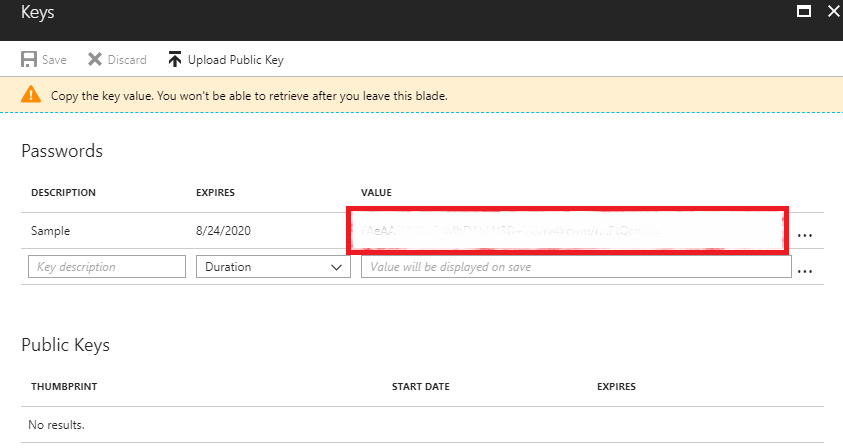
2.1 - Select Keys and fill in the DESCRIPTION and EXPIRES fields. Once we save the key we will get its value. This will be the key with which we will authenticate our application in order to use the API.
Wazuh configuration
Next we will see the options we have for configuring the integration.
3. azure-logs module configuration
Note
When we choose to use a file for authentication, its content must be field = value. For example:
application_id = 8b7...c14
application_key = w22...91x
3.1 - We opted for the following example configuration. The integration will be executed every Friday at 12:00. Authentication will be carried out by reading the file containing the credentials. We add a representative tag and set the search for the activities/audit?api-version=beta query to give us the results of the previous day.
<wodle name="azure-logs">
<disabled>no</disabled>
<wday>Friday</wday>
<time>12:00</time>
<run_on_start>no</run_on_start>
<graph>
<auth_path>/home/manager/Azure/graph_auth.txt</auth_path>
<tenantdomain>wazuh.onmicrosoft.com</tenantdomain>
<request>
<tag>azure-active_directory</tag>
<query>activities/audit?api-version=beta</query>
<time_offset>1d</time_offset>
</request>
</graph>
</wodle>
You can see the wodle reference here.
The field tenantdomain is necessary and we can obtain it easily. In the azure portal, we can see it leaving the cursor in the upper right corner.

Azure Active Directory Graph Use Case
Using the configuration prepared above, we will show an example of use.
Wazuh Rules
As the records are in .json format, with this rule, already included in the integration, we can start generating alerts:
<rule id="87802" level="3">
<decoded_as>json</decoded_as>
<field name="azure_tag">azure-ad-graph</field>
<description>Azure: AD $(activity)</description>
</rule>
Create a new user
Proceed to create a new user. If the creation is successful, a log will be written to reflect it.
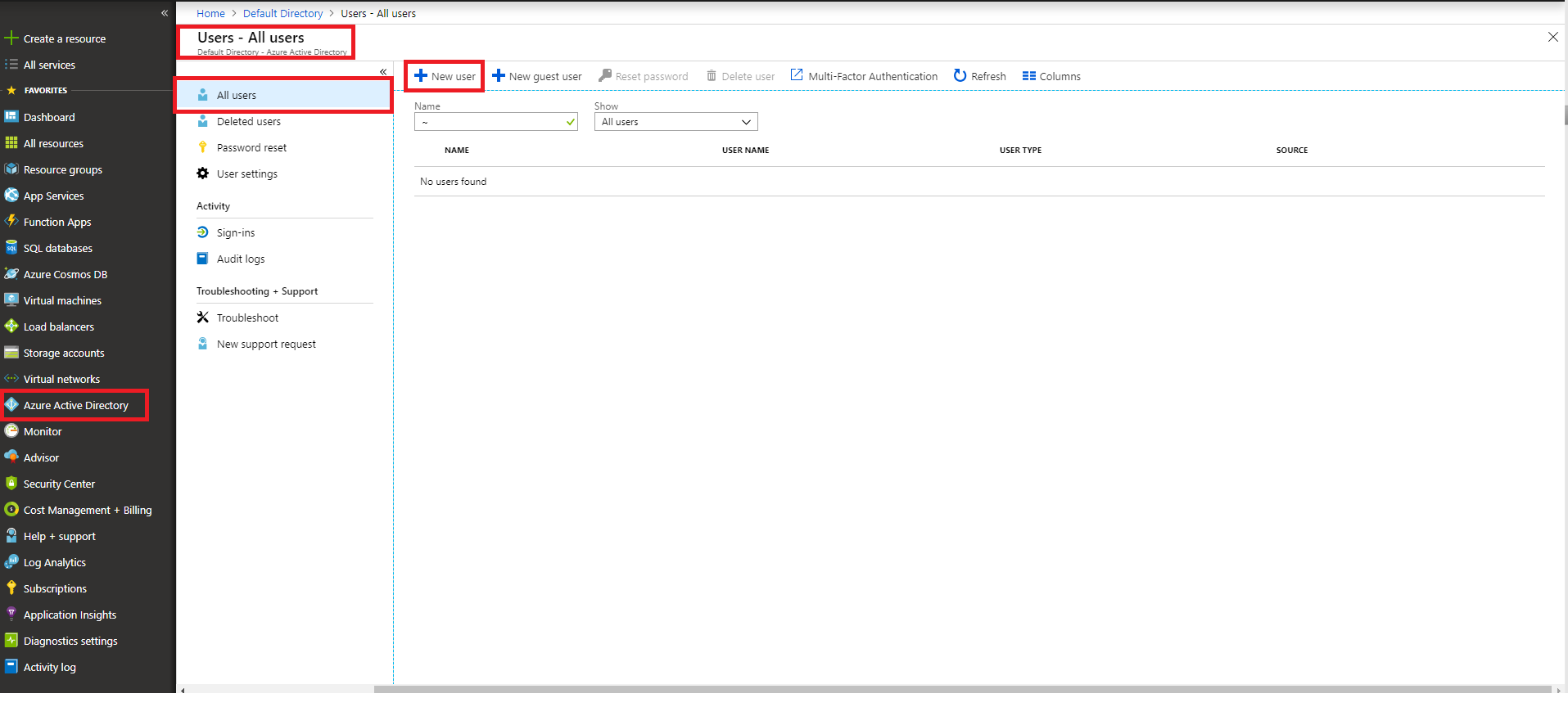
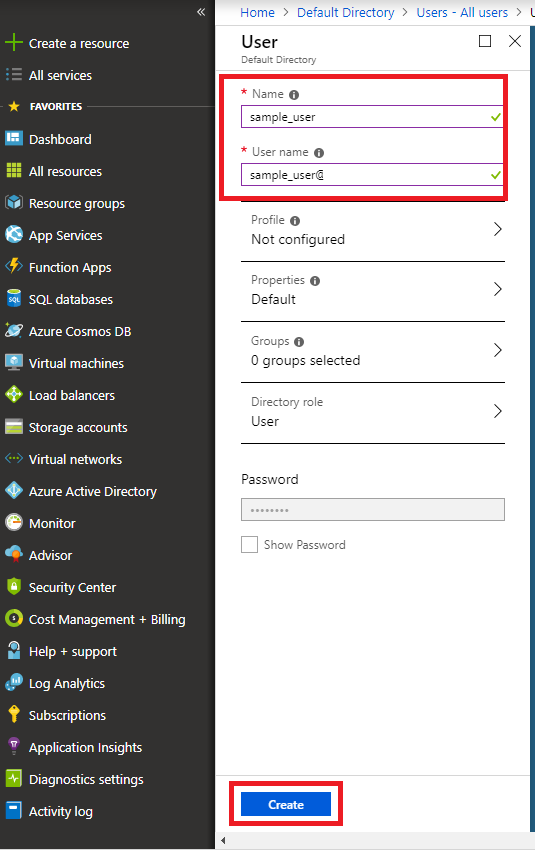
Azure portal visualization
From the Azure Active Directory entry select the Audit logs entry and we can see the creation of our user.
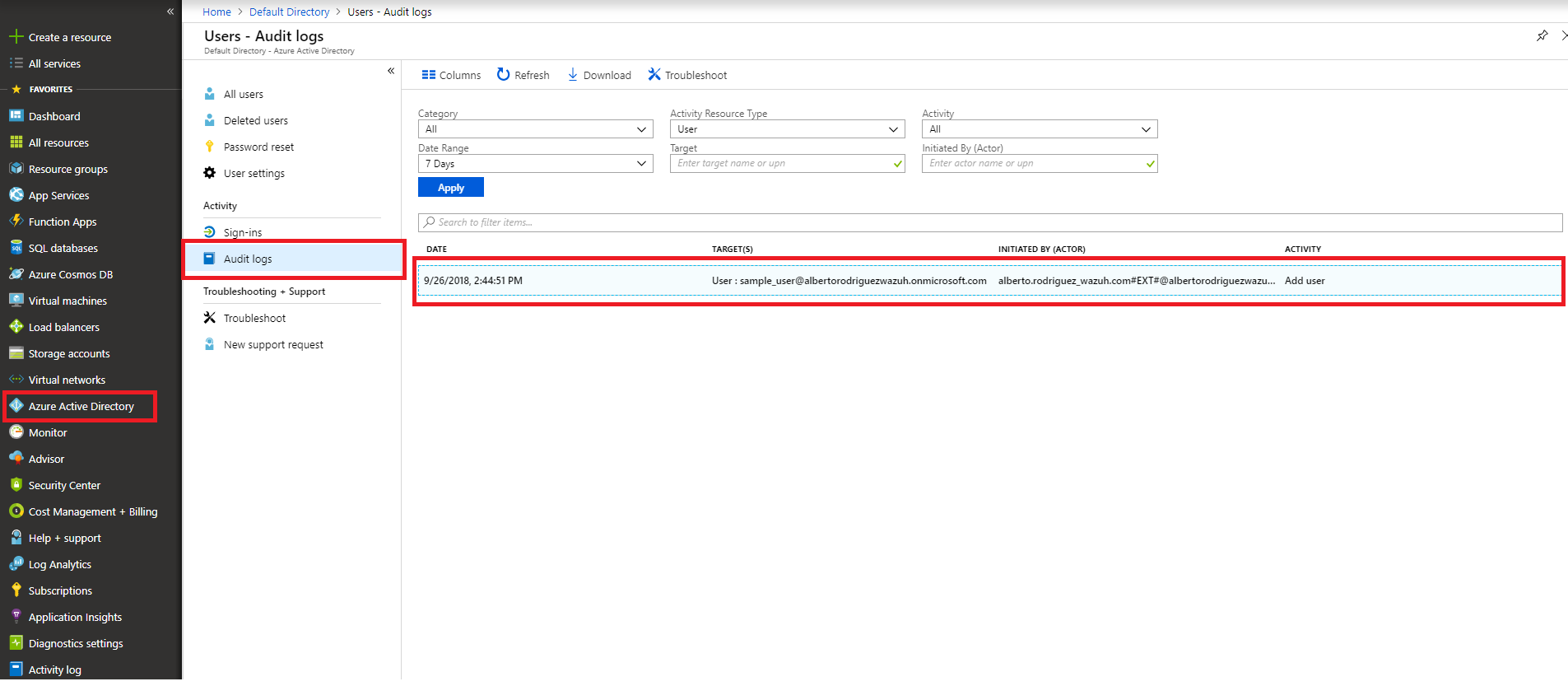
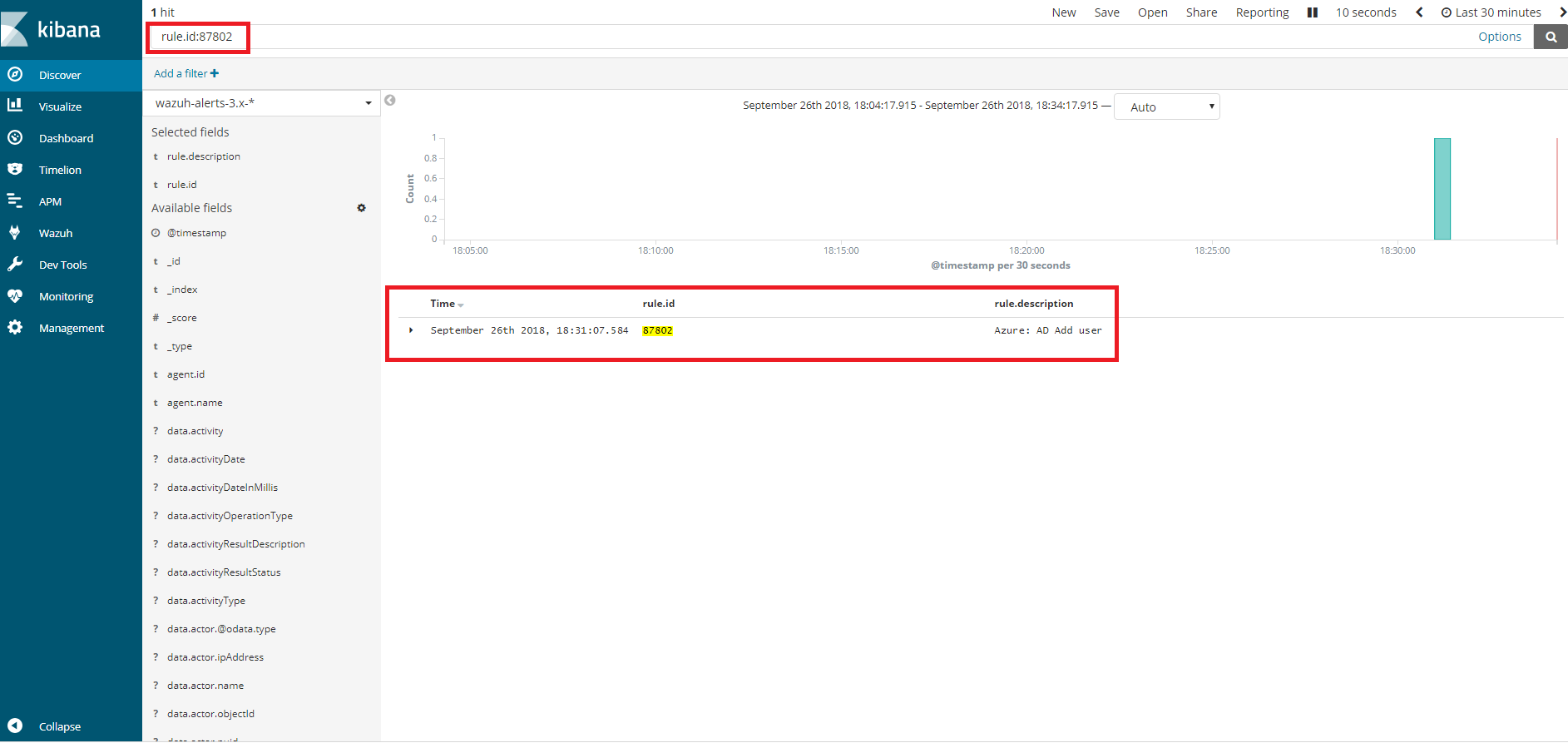
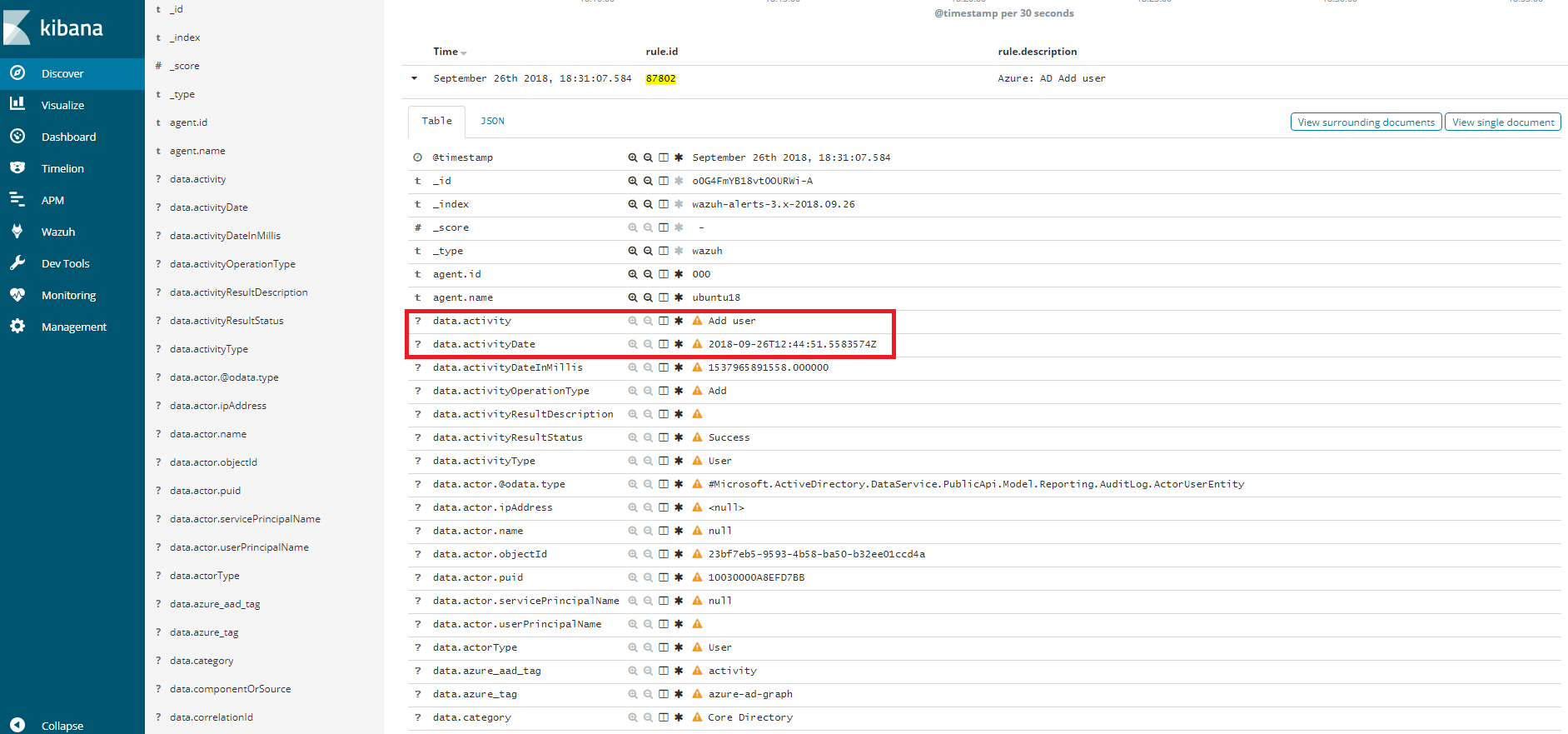
Kibana visualization
When our integration performs the query, we will be able to see the results in Kibana. As we can see through the rule 87802 the dates of the events coincide (taking into consideration the time difference between computers).