Detecting suspicious binaries
Wazuh provides you with powerful anomaly and malware detection capabilities to detect suspicious binaries. In this POC, you detect trojaned system binaries by using signatures in the /var/ossec/etc/shared/rootkit_trojans.txt file.
Configuration
Configure your environment as follows to test the POC.
No additional configuration is required since trojan detection is configured out-of-the-box. Check your configuration in the /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf file at the CentOS 8 monitored endpoint.
<rootcheck> <disabled>no</disabled> <check_files>yes</check_files> <!-- Line for trojans detection --> <check_trojans>yes</check_trojans> <check_dev>yes</check_dev> <check_sys>yes</check_sys> <check_pids>yes</check_pids> <check_ports>yes</check_ports> <check_if>yes</check_if> <!-- Frequency that rootcheck is executed - every 12 hours --> <frequency>43200</frequency> <rootkit_files>/var/ossec/etc/shared/rootkit_files.txt</rootkit_files> <rootkit_trojans>/var/ossec/etc/shared/rootkit_trojans.txt</rootkit_trojans> <skip_nfs>yes</skip_nfs> </rootcheck>
Steps to generate the alerts
Create a copy of the original system binary.
# cp -p /usr/bin/w /usr/bin/w.copy
Replace the original system binary
/usr/bin/wwith the following shell script.#!/bin/bash echo "`date` this is evil" > /tmp/trojan_created_file echo 'test for /usr/bin/w trojaned file' >> /tmp/trojan_created_file #Now running original binary /usr/bin/w.copy
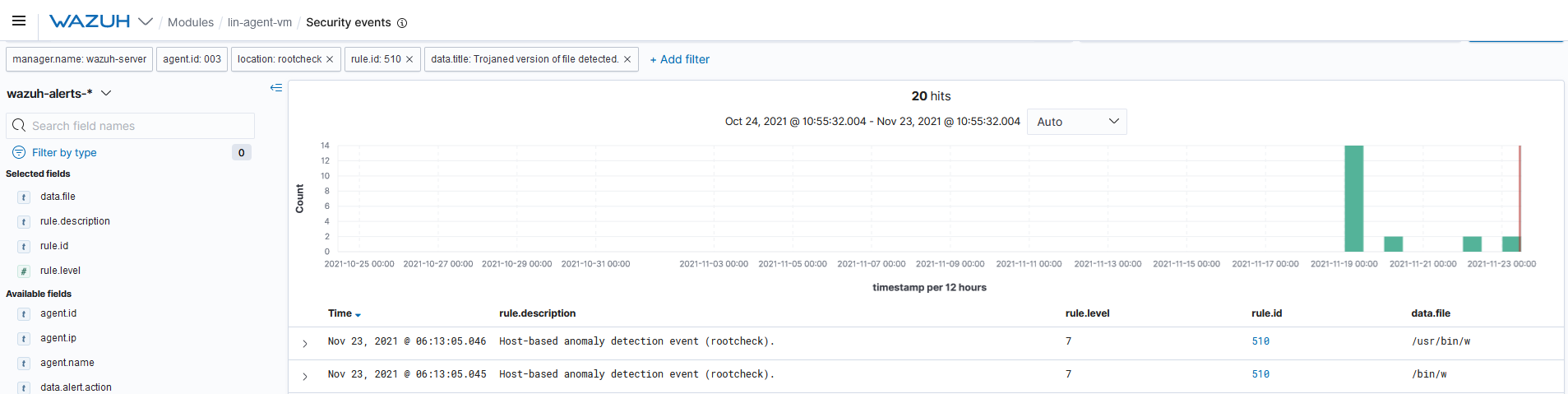
Query the alerts
You can visualize the alert data in the Wazuh Kibana plugin. To do this, go to the Security events module and add the filters in the search bar to query the alerts.
location:rootcheck AND rule.id:510 AND data.title:Trojaned version of file detected