AWS Config
AWS Config is a service that enables you to assess, audit, and evaluate the configurations of your AWS resources. AWS Config continuously monitors and records your AWS resource configurations and allows you to automate the evaluation of recorded configurations against desired configurations. With AWS Config, you can review changes in configurations and relationships between AWS resources, dive into detailed resource configuration histories, and determine your overall compliance against the configurations specified in your internal guidelines. This enables you to simplify compliance auditing, security analysis, change management, and operational troubleshooting.
Amazon configuration
The following sections cover how to configure different services required to integrate AWS config service with Wazuh.
Amazon Data Firehose configuration
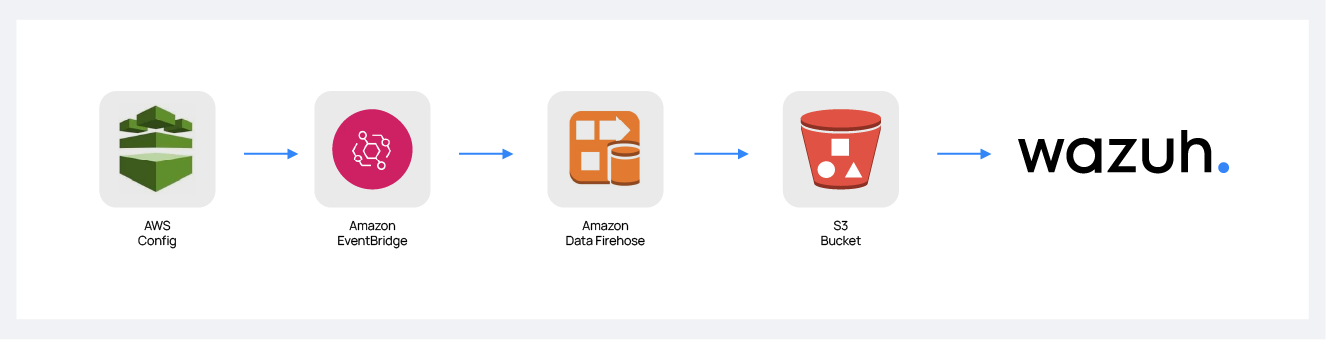
Create an Amazon Data Firehose delivery stream to store the AWS Config events into the desired S3 bucket so Wazuh can process them.
Create a new S3 bucket. If you want to use an already existing one, skip this step.
On your AWS console, search for "amazon data firehose" in the search bar at the top of the page or go to Services > Analytics > Amazon Data Firehose.
Click Create Firehose stream.
Select Direct PUT and Amazon S3 as the desired Source and Destination, respectively.
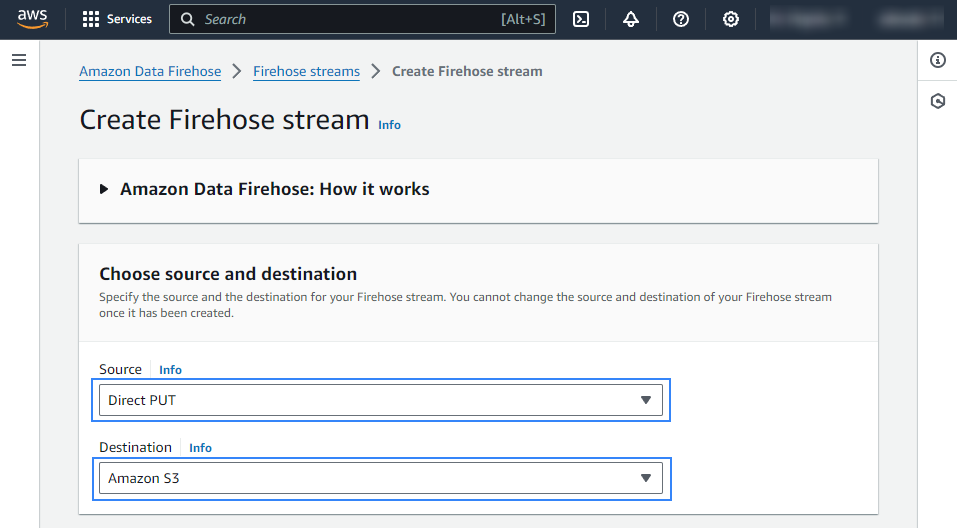
Choose an appropriate Firehose stream name.
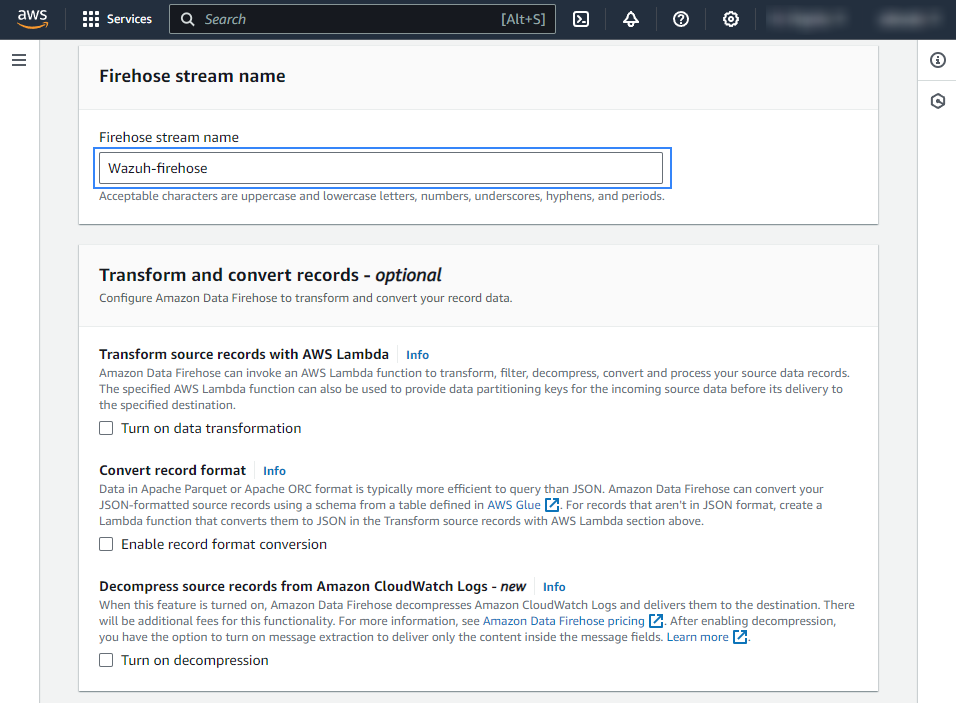
Select the desired S3 bucket as the destination. It is possible to specify a custom prefix to alter the path where AWS stores the logs. AWS Firehose creates a file structure
YYYY/MM/DD/HH, if a prefix is used the created file structure would beprefix-name/YYYY/MM/DD/HH. If a prefix is used it must be specified under the Wazuh bucket configuration. Select your preferred compression, Wazuh supports any kind of compression but Snappy.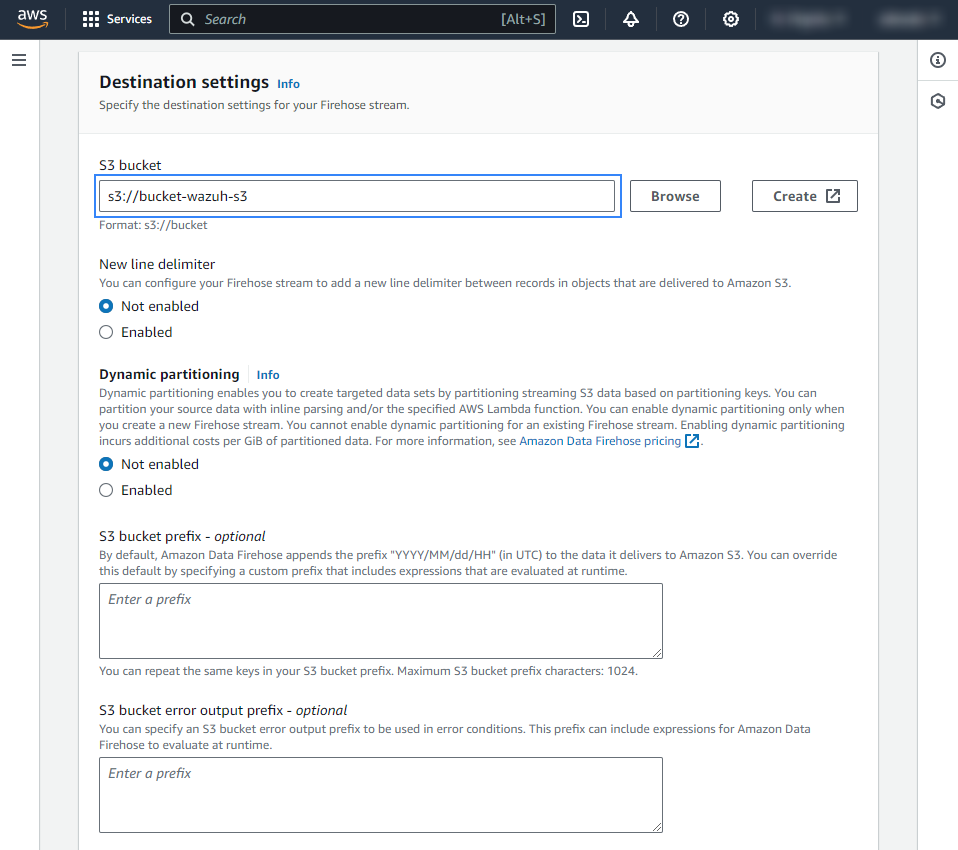
Create or choose an existing IAM role to be used by Amazon Data Firehose in the Advanced settings section.
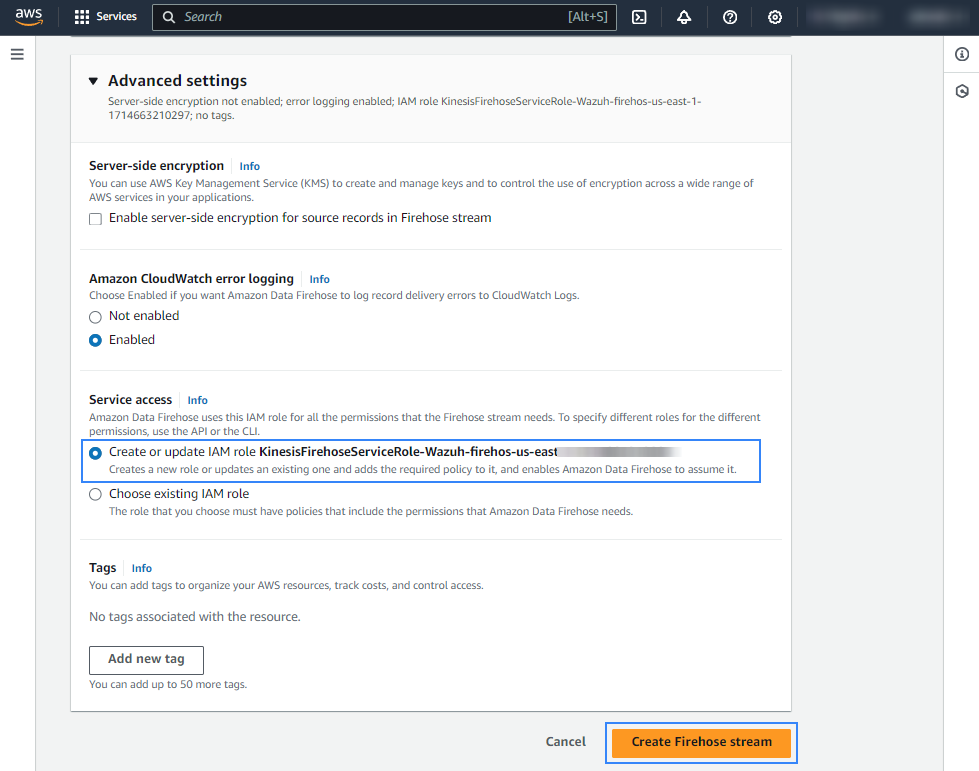
Click Create Firehose stream at the end of the page. The new delivery stream will be created and its details will be shown as follows.
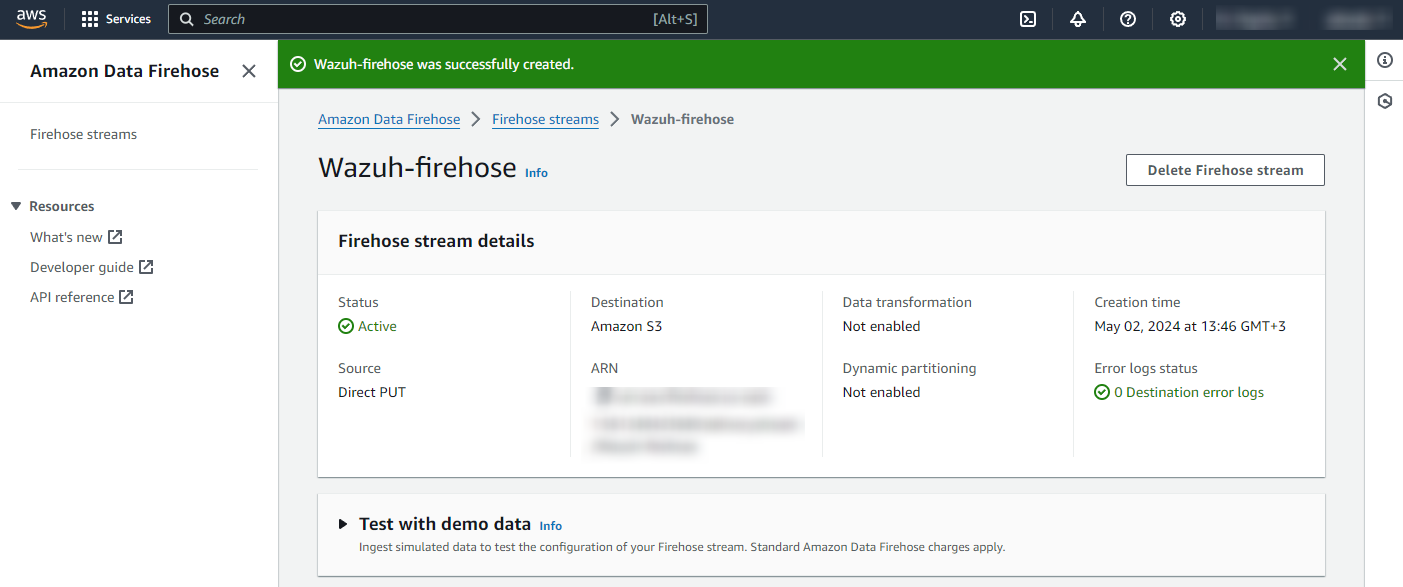
AWS Config configuration
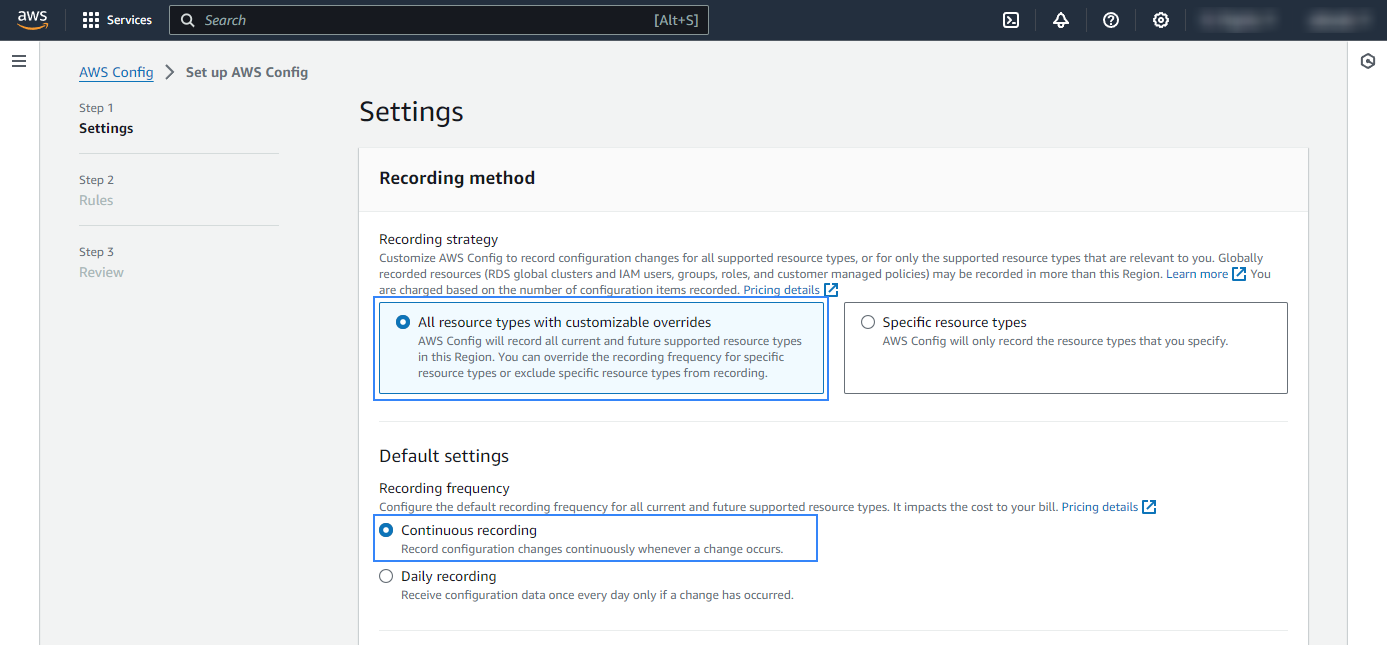
On the AWS Config page, go to Set up AWS Config.
Under Recording strategy, specify the AWS resource types you want AWS Config to record:
All resource types with customizable overrides
Specific resource types
Note
For more information about these options, see selecting which resources AWS Config records.
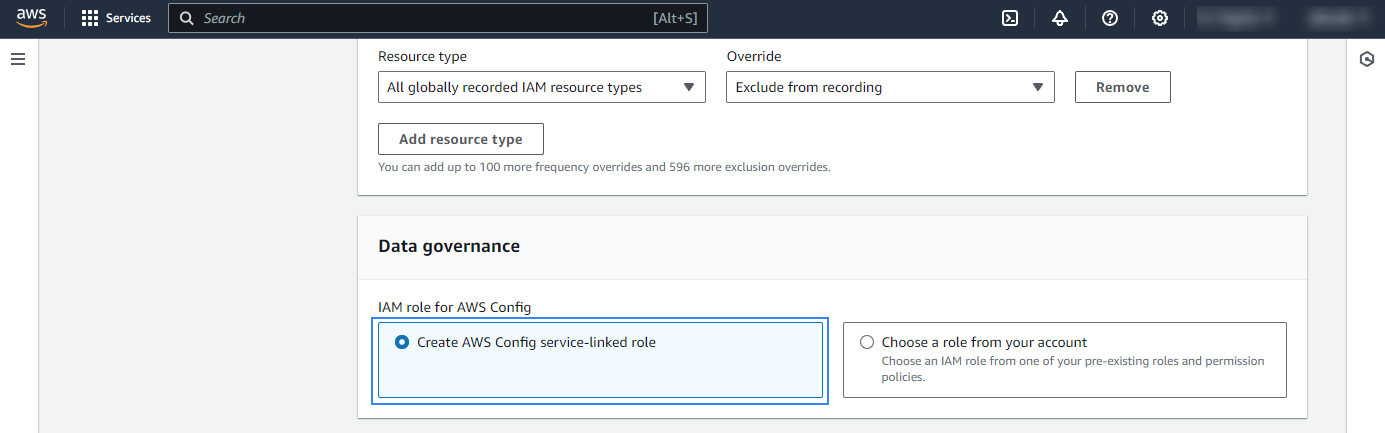
Create or select an existing IAM role for AWS Config.
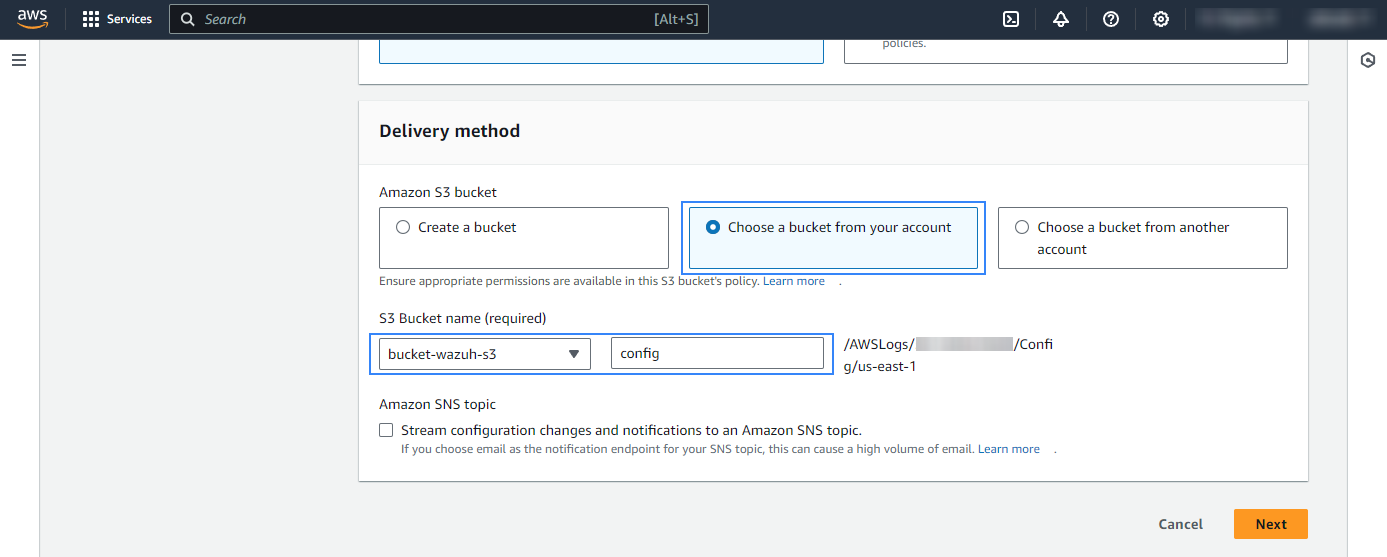
Select an existing S3 bucket and prefix or create a new one then save your configuration.
After these steps, it is necessary to configure an Amazon EventBridge rule to send AWS config events to the Amazon Data Firehose delivery stream created in the previous step.
Amazon EventBridge configuration
Configure an Amazon EventBridge rule to send Config events to the Amazon Data Firehose delivery stream created in the previous step.
On your AWS console, search for "eventbridge" in the search bar at the top of the page or go to Services > Application Integration > EventBridge.
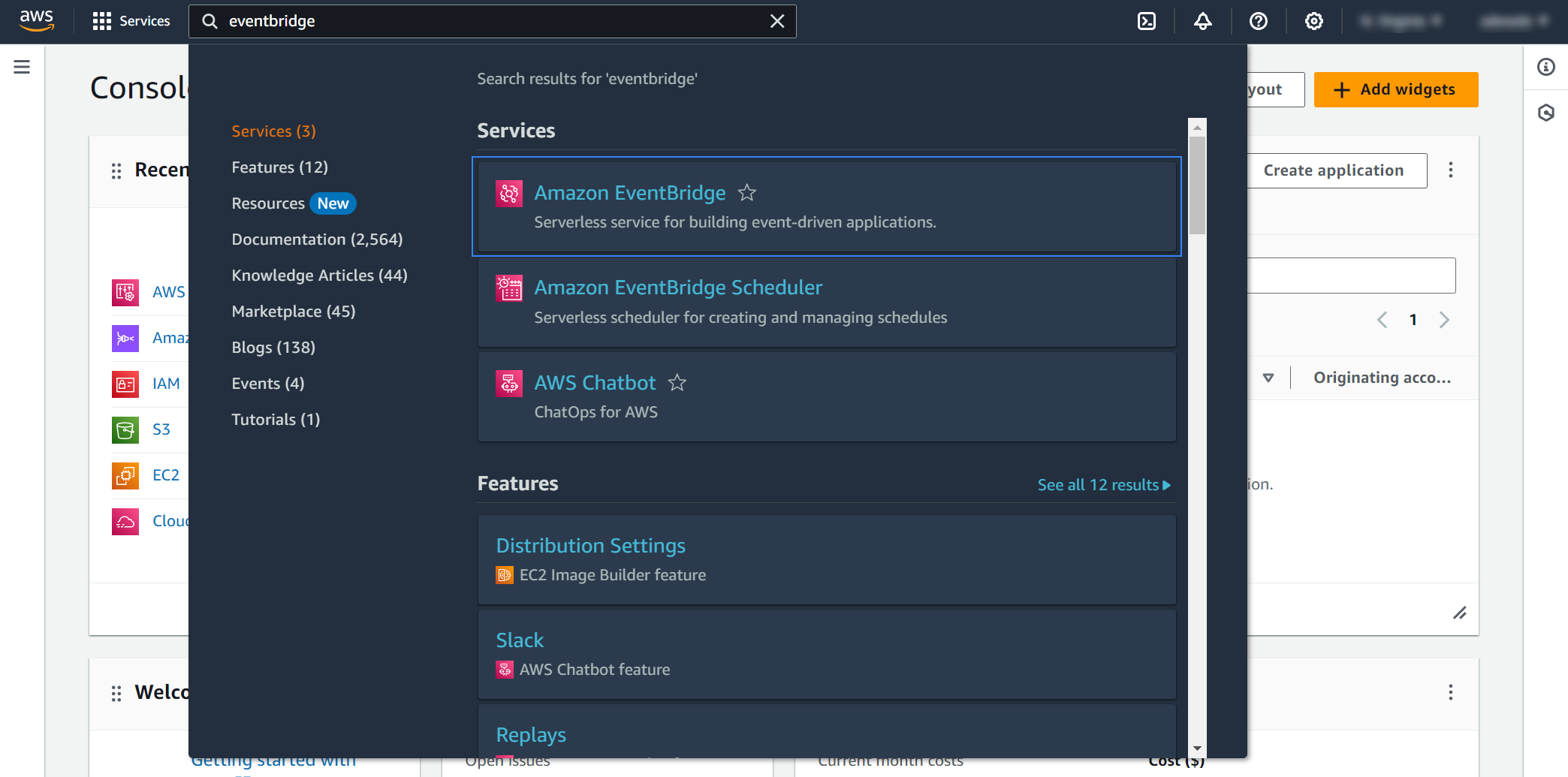
Select EventBridge Rule and click Create rule.
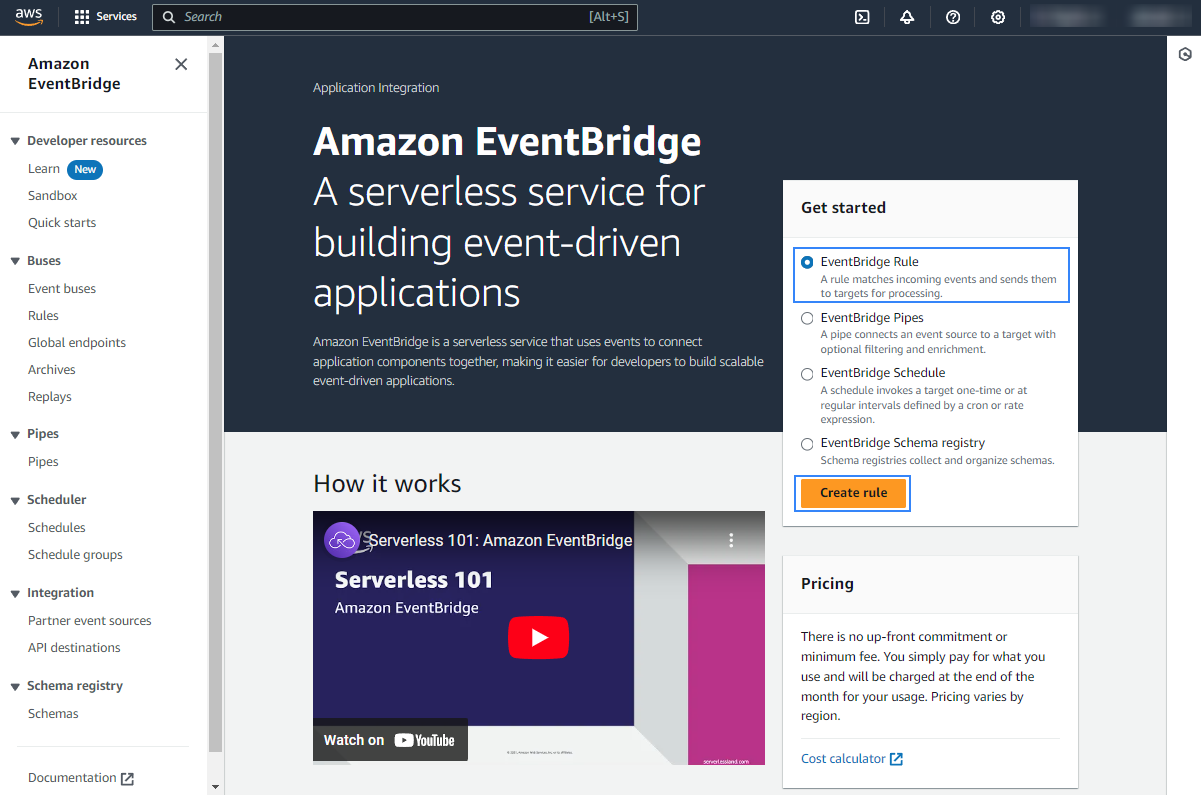
Assign a name to the EventBridge rule and select the Rule with an event pattern option.
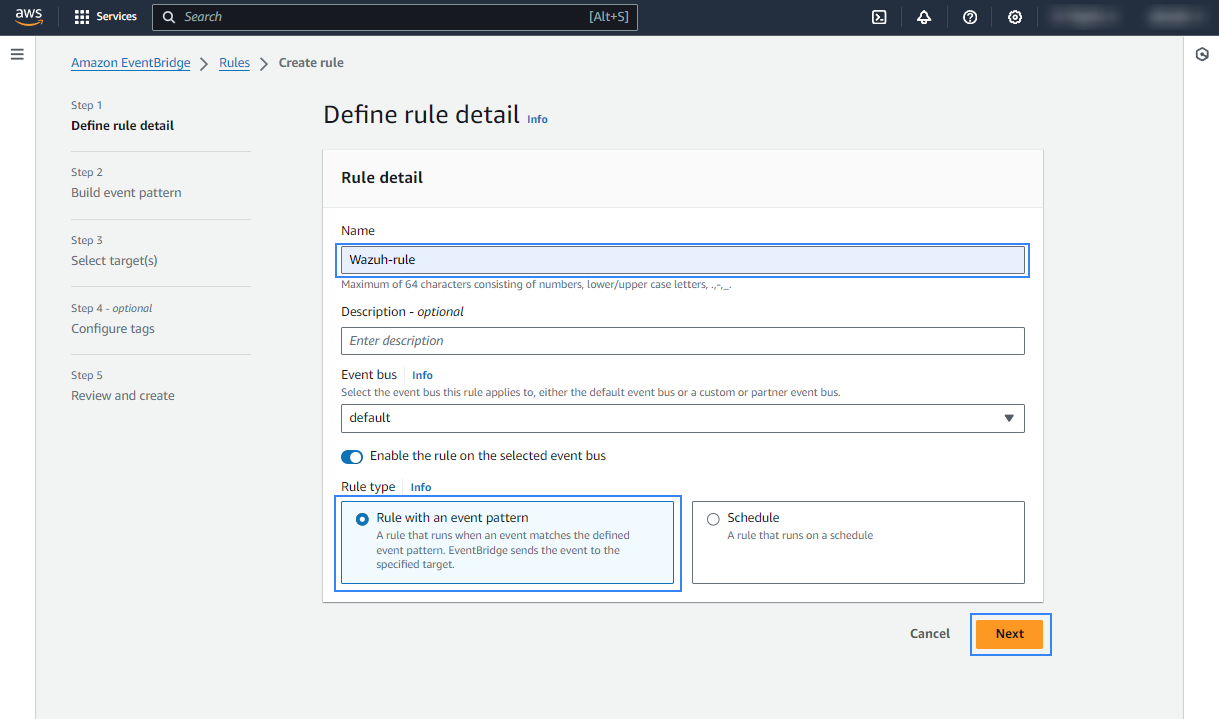
In the Build event pattern section, choose AWS events or EventBridge partner events as Event source.
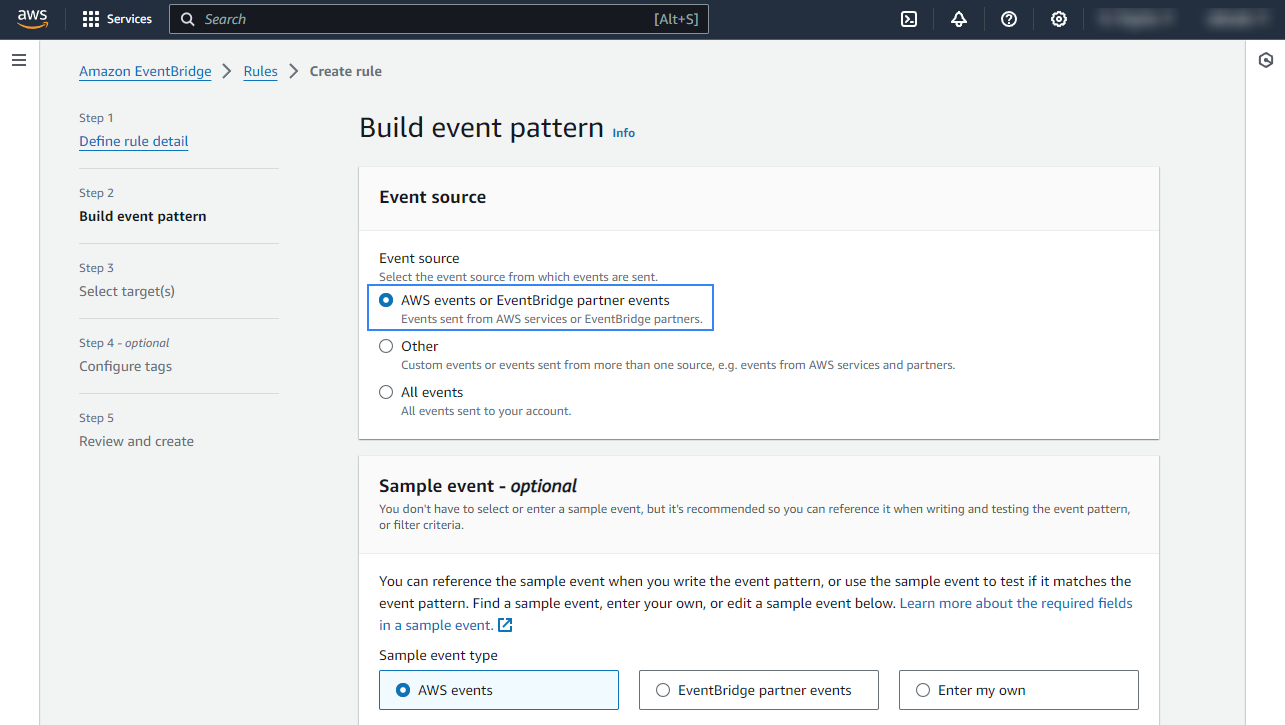
In the Event pattern section choose AWS services as Event source, Config as AWS service, and All Events as Event type. Click Next to apply the configuration.
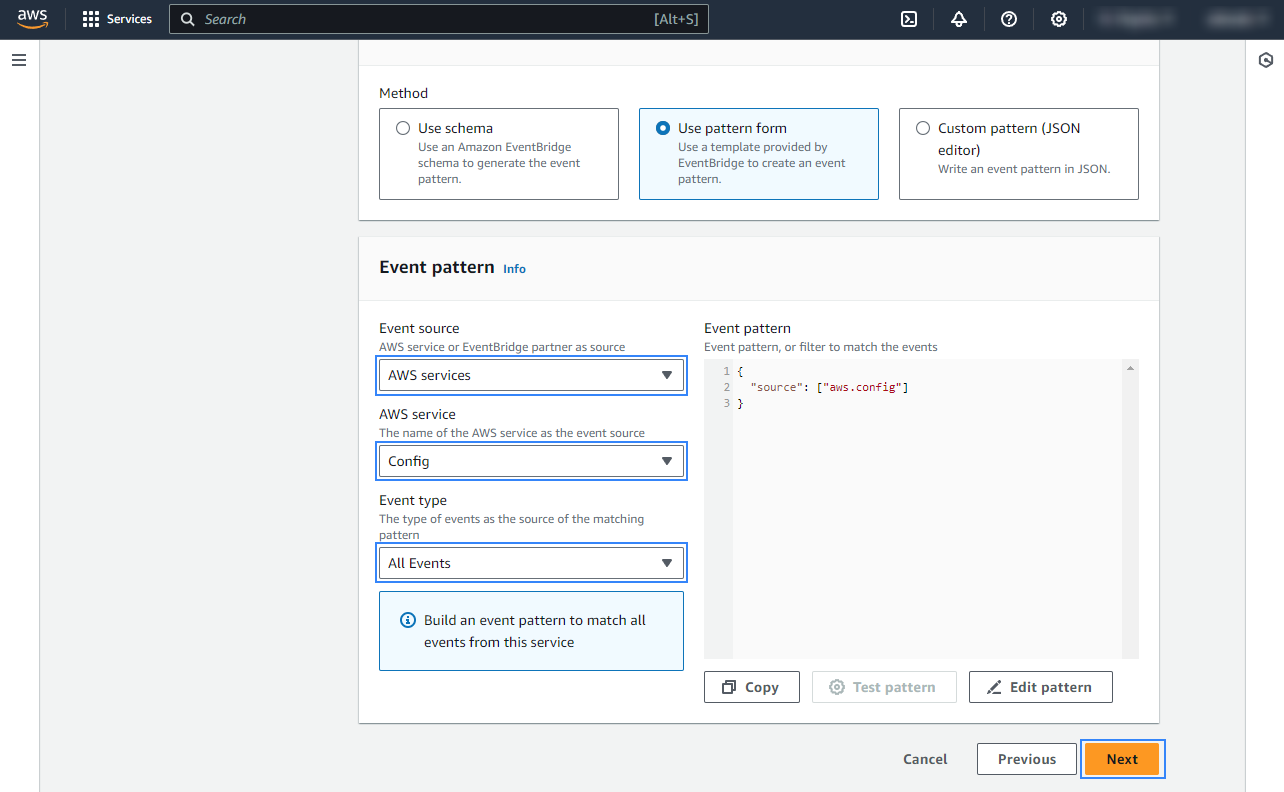
Under Select a target, choose Firehose delivery stream and select the stream created previously. Also, create a new role to access the delivery stream. Click Next to apply the configuration.
Review the configuration and click Create rule.
Once the rule is created, every time an AWS Config event is sent, it will be stored in the specified S3 bucket. Remember to first enable the AWS Config service, otherwise, you won't get any data.
Policy configuration
Follow the creating an AWS policy guide to create a policy using the Amazon Web Services console.
Take into account that the policies below follow the principle of least privilege to ensure that only the minimum permissions are provided to the AWS IAM user.
To allow an AWS user to use the Wazuh module for AWS with read-only permissions, it must have a policy like the following attached:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::<WAZUH_AWS_BUCKET>/*",
"arn:aws:s3:::<WAZUH_AWS_BUCKET>"
]
}
]
}
If it is necessary to delete the log files once they have been collected, the associated policy would be as follows:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:DeleteObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::<WAZUH_AWS_BUCKET>/*",
"arn:aws:s3:::<WAZUH_AWS_BUCKET>"
]
}
]
}
Note
<WAZUH_AWS_BUCKET> is a placeholder. Replace it with the actual name of the bucket from which you want to retrieve logs.
After creating a policy, you can attach it directly to a user or to a group to which the user belongs. In attaching a policy to an IAM user group, you see how to attach a policy to a group. More information on how to use other methods is available in the AWS documentation.
Configure Wazuh to process Amazon Config logs
Access the Wazuh configuration in Server management > Settings using the Wazuh dashboard or by manually editing the
/var/ossec/etc/ossec.conffile in the Wazuh server or agent.
Add the following Wazuh module for AWS configuration to the file, replacing
<WAZUH_AWS_BUCKET>with the name of the S3 bucket:<wodle name="aws-s3"> <disabled>no</disabled> <interval>10m</interval> <run_on_start>yes</run_on_start> <skip_on_error>yes</skip_on_error> <bucket type="config"> <name><WAZUH_AWS_BUCKET></name> <path>config</path> <aws_profile>default</aws_profile> </bucket> </wodle>
Note
In this example, the
aws_profileauthentication parameter was used. Check the credentials section to learn more about the different authentication options and how to use them.Save the changes and restart Wazuh to apply the changes. The service can be manually restarted using the following command outside the Wazuh dashboard:
Wazuh manager:
# systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Wazuh agent:
# systemctl restart wazuh-agent
Use cases
AWS Config allows you to review changes in configuration and relationships between AWS resources. Below is an example of a use case for AWS Config.
Monitoring configuration changes
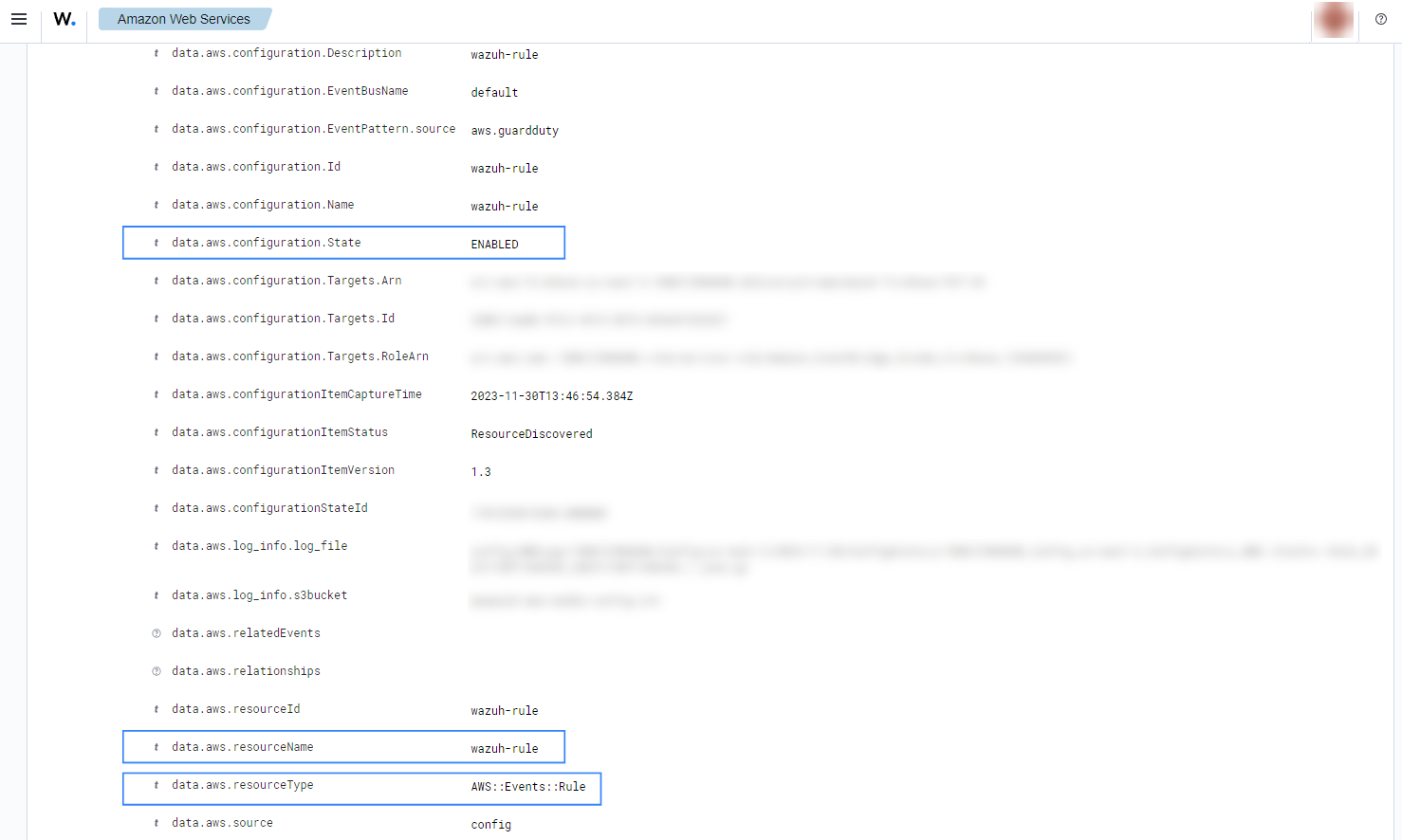
Multiple alerts with rule ID 80454 will be seen on the Wazuh dashboard when there are changes in the configuration of the resources monitored by AWS config. Some examples are shown in the image below.
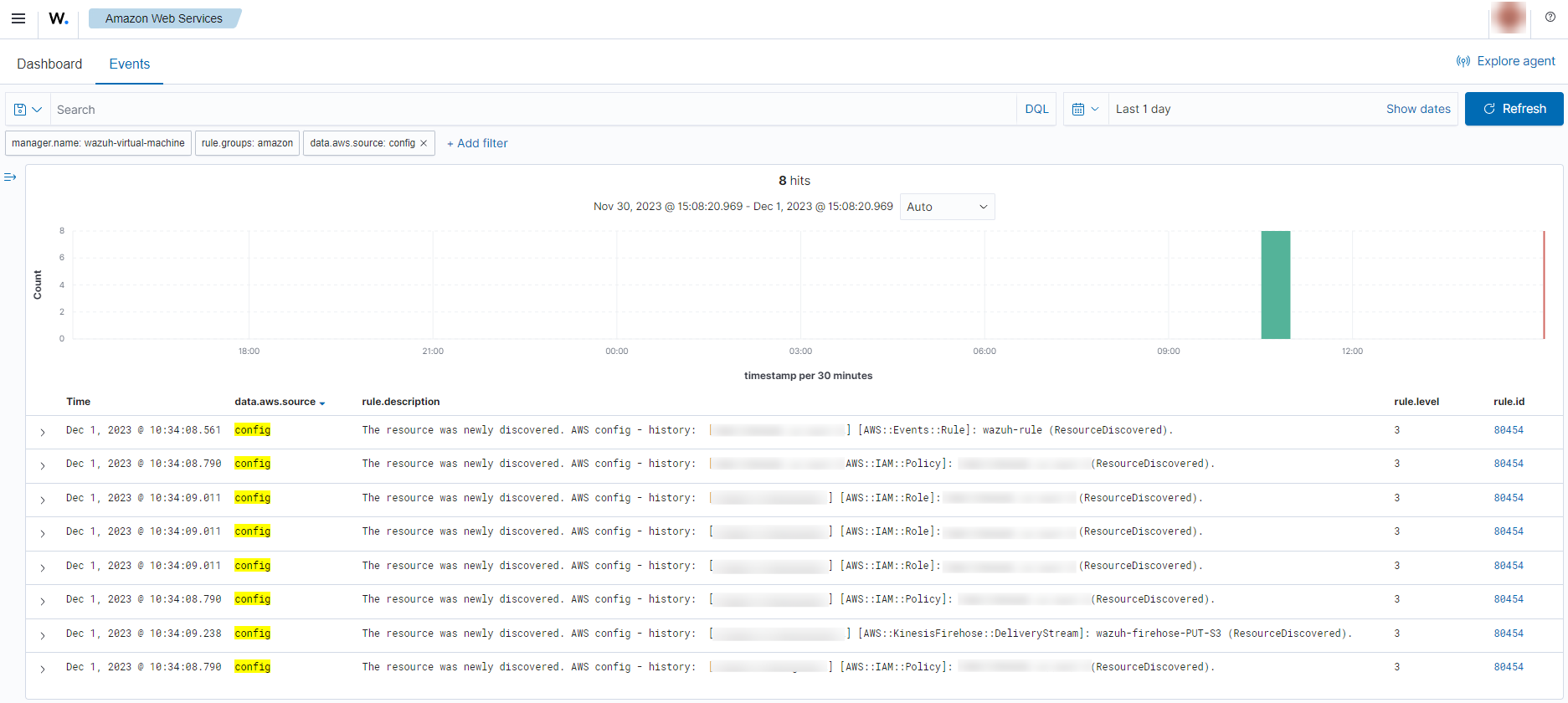
You can expand an alert to see more information such as the resource name, resource type, and configuration state.