AWS Security Hub
AWS Security Hub automates security best practice checks and aggregates insights to help users understand their overall security posture across multiple AWS accounts. Security Hub helps users assess their compliance against security best practices. It achieves this by:
Running checks against security controls.
Generating control findings.
Grouping related findings into collections called insights.
You need to perform the following to set up the integration that allows you to receive Security Hub events on your Wazuh environment:
Configure your AWS environment. This involves:
Enabling Amazon Security Hub. There are two methods to enable Amazon Security Hub in your environment. Please see the enabling Security Hub section.
Creating a Firehose stream: The Amazon EventBridge is a serverless event bus service that makes it easy to connect applications using events from AWS services, integrated SaaS applications, and custom sources in real-time. EventBridge needs a target such as the Firehose stream. It triggers the target when it receives an event matching an event pattern defined in the rule.
Integrating Security Hub with EventBridge: EventBridge allows storing Security Hub findings and insights in S3 buckets.
Enabling an Amazon S3 bucket to include event notifications: The bucket sends notifications to the queue for every Security Hub object creation event.
Enabling an Amazon SQS queue: The Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) is a message queuing service that enables decoupled communication between AWS components. The Wazuh module for AWS will query the SQS for notifications of created logs in S3 and generate alerts from Security Hub logs.
Configure the Wazuh module for AWS to receive Amazon Security Hub events.
Amazon configuration
Enabling Security Hub
Search for the “Security Hub” using the AWS console search bar to determine the best method that suits your environment. There are two ways to enable AWS Security Hub:
Manual Integration: We recommend this method for standalone accounts with a single organization. The screenshot below shows how to enable AWS Security Hub using the AWS Security Hub console. Please follow the enabling Security Hub manually guideline to find other methods to enable the AWS Security Hub.
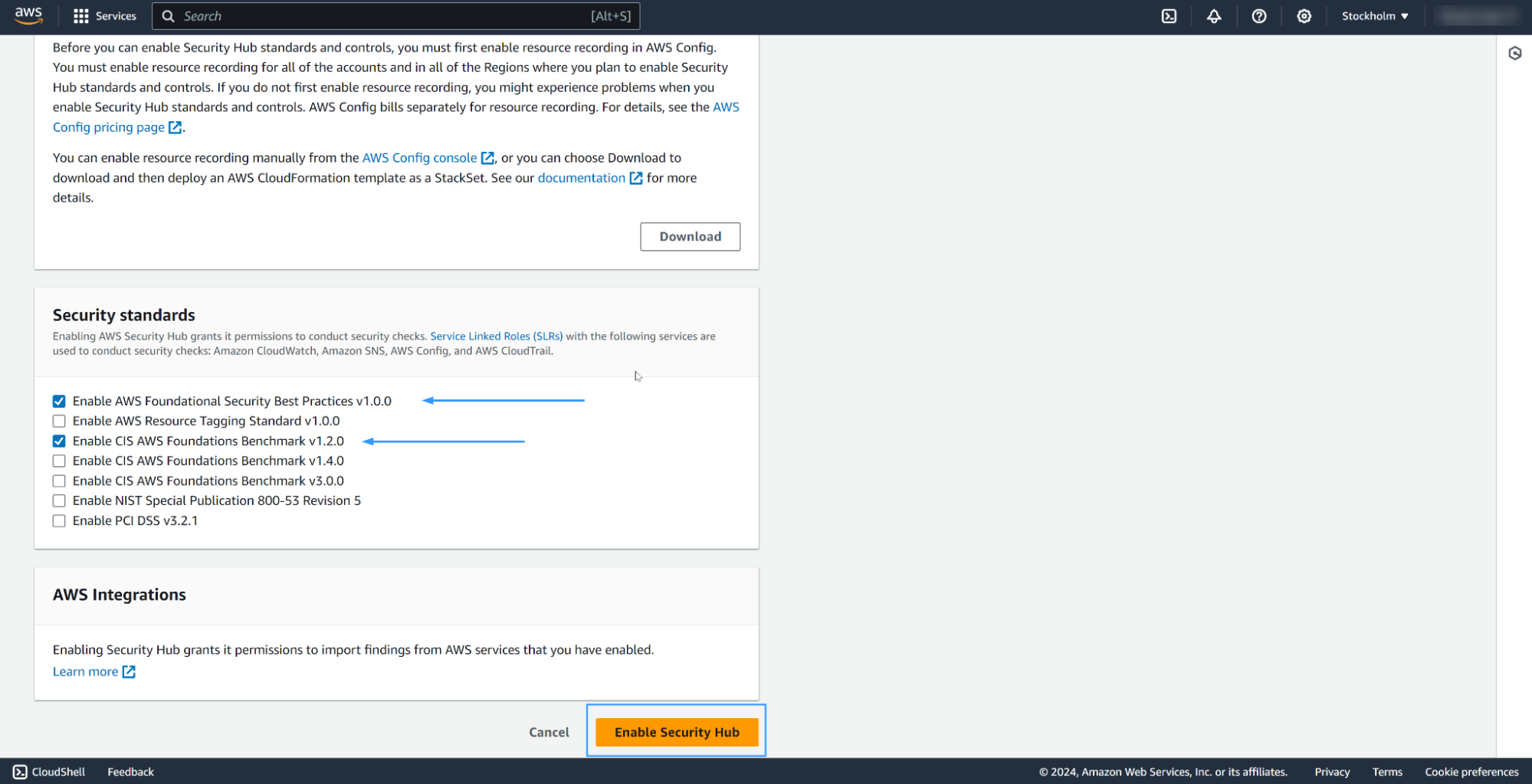
Organizations integration: We recommend this method for multi-account and multi-region environments. Your organization must have a delegated administrator account. Please follow the enabling Security Hub with organizations integration guidelines to set your AWS Security Hub using this method.
Creating a Firehose stream
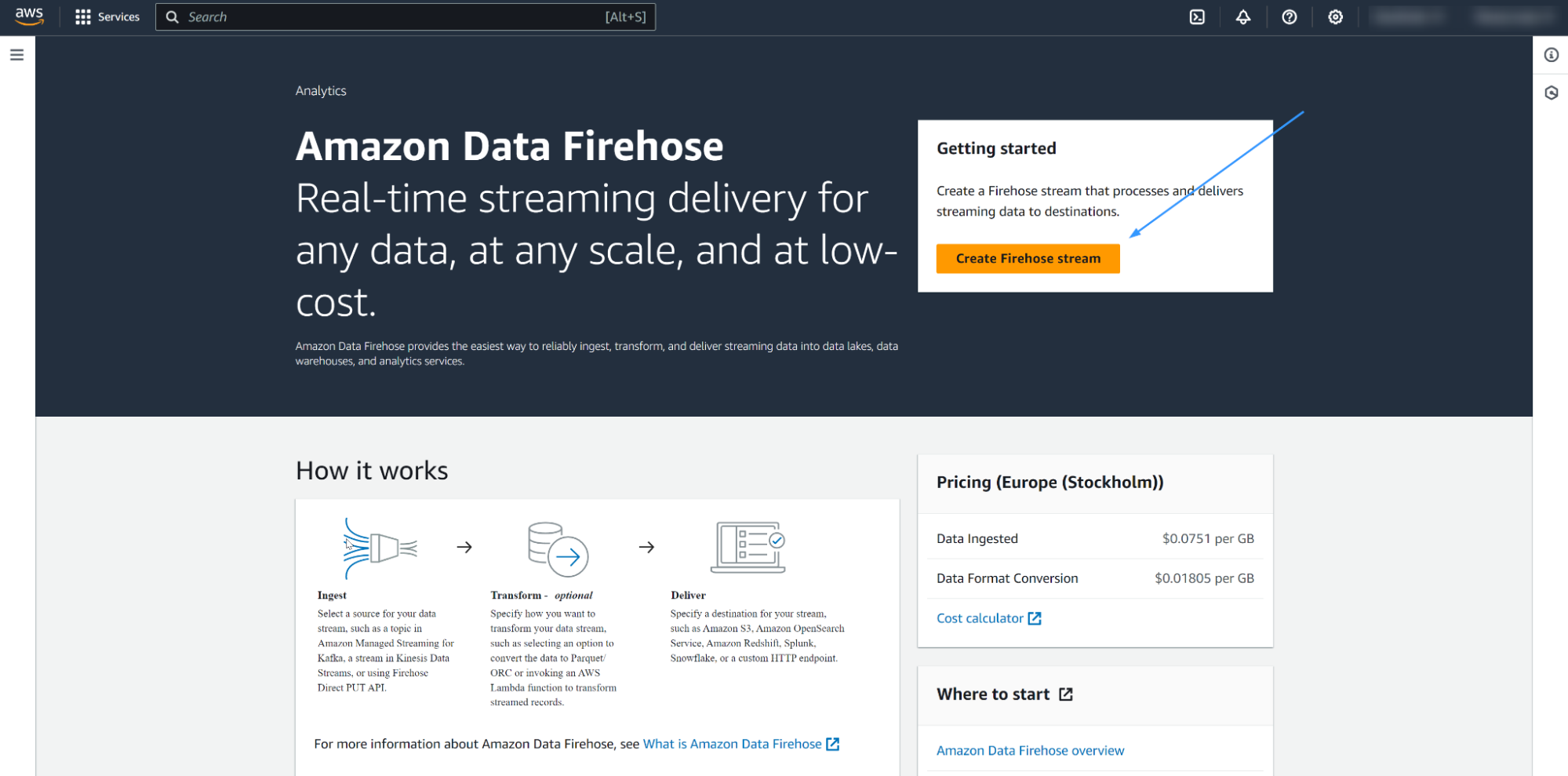
The Amazon Firehose stream serves as the channel for sending the AWS Security Hub logs to the S3 bucket. Follow the steps below to create an Amazon Firehose stream for your Amazon Security Hub logs.
Go to the Amazon Data Firehose service and click Create Firehose stream.
Select Direct PUT as the source and Amazon S3 as the destination.
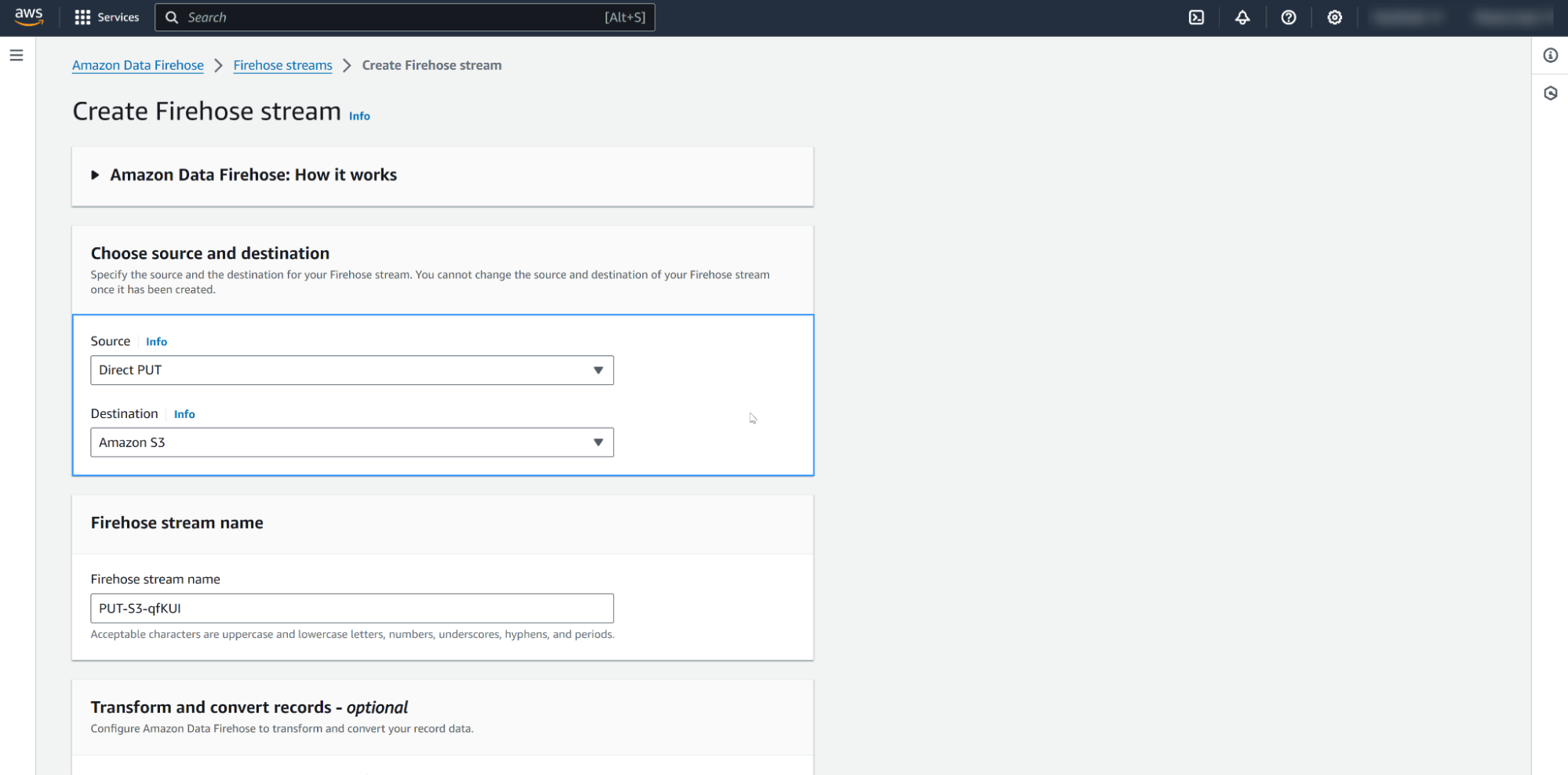
Choose or create your proposed Amazon S3 bucket. You can use an Amazon S3 bucket prefix, but this is optional.
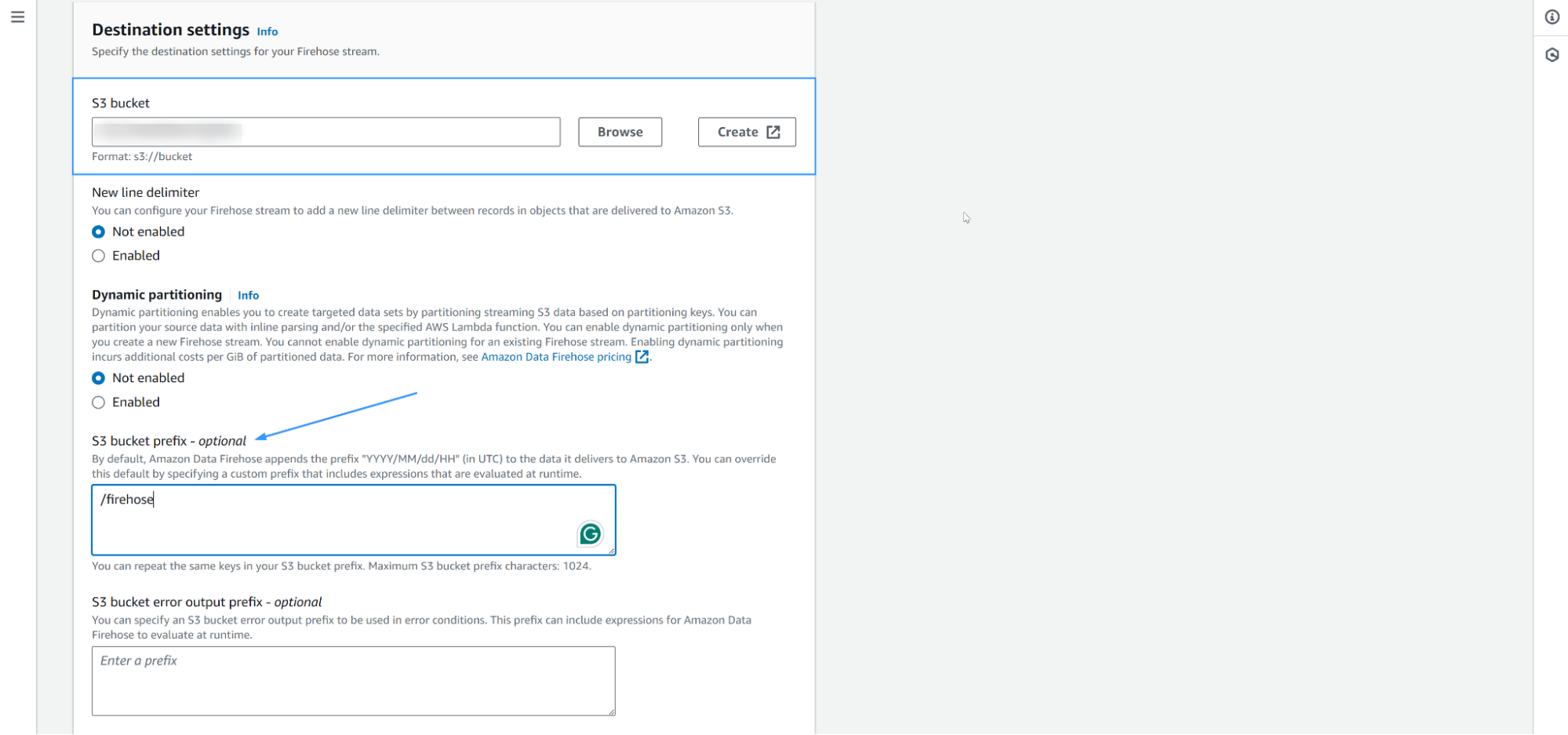
Click Create Firehose stream.
Integrating Security Hub with EventBridge
Integrating Security Hub with EventBridge enables the storage of Security Hub events in S3 buckets.
There are three types of events available, each using a specific Eventbridge event format. The Wazuh integration takes every relevant detail and detail-type value from them.
Security Hub Findings - Imported: Security Hub automatically sends events of this type to EventBridge. They include new findings and updates to existing findings, each containing a single finding.
Security Hub Findings - Custom Action: When you trigger custom actions, Security Hub sends these events to EventBridge. The custom actions associate the events with their findings.
Security Hub Insight Results: This event processes the Security Hub Insights. You can use custom actions to send sets of insight results to EventBridge. Insight results are the resources that match an insight.
To send the last two types of events to EventBridge, you need to create a custom action in Security Hub. Please refer to the Amazon Security Hub documentation to achieve this. Find more information about the types of Security Hub integration with EventBridge.
To integrate Security Hub with EventBridge, you must create an event rule in EventBridge.
Go to the Amazon EventBridge and create a new EventBridge rule.
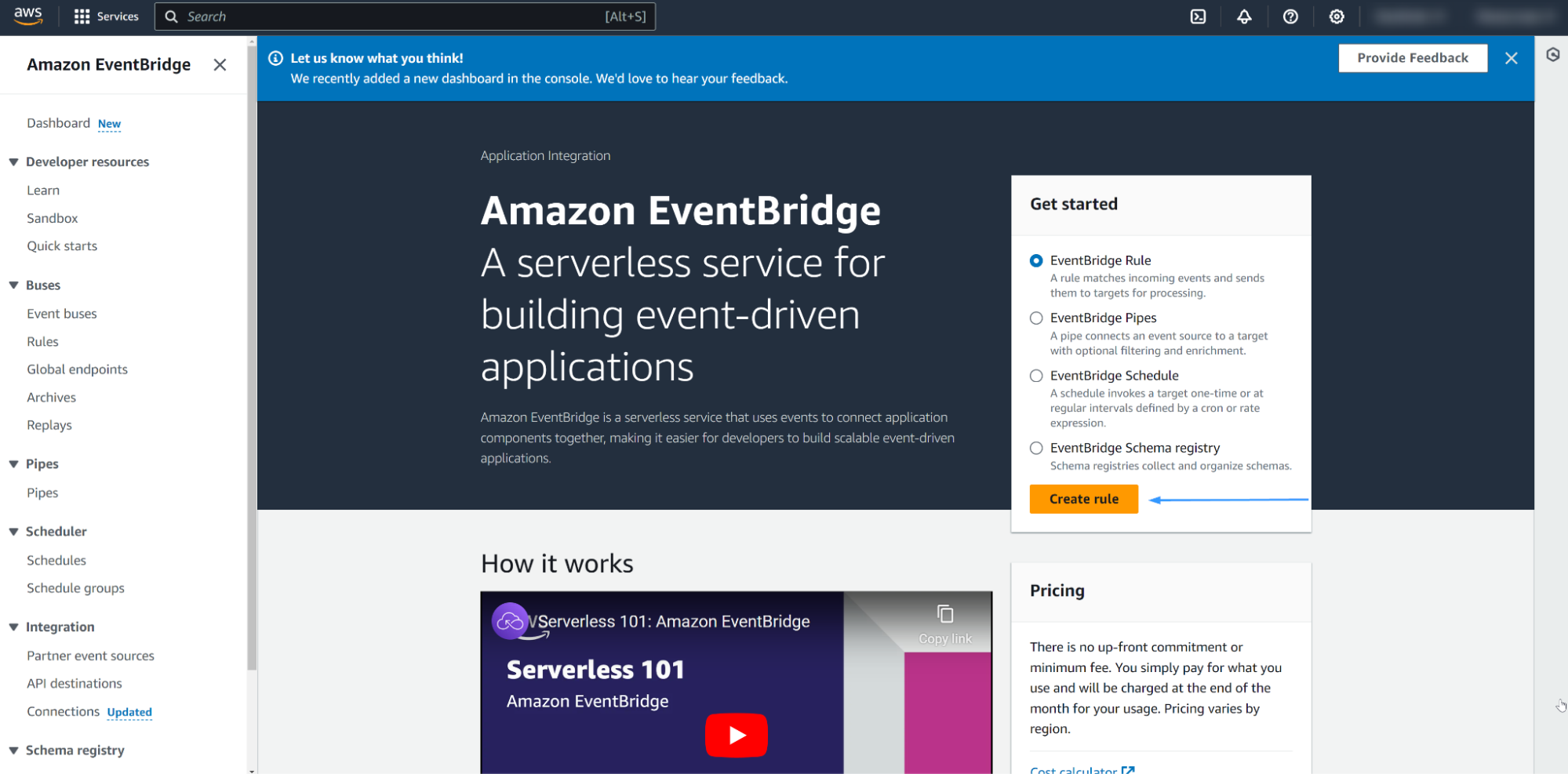
Enter a name for the rule and select Rule with an event pattern. Then click on Next.
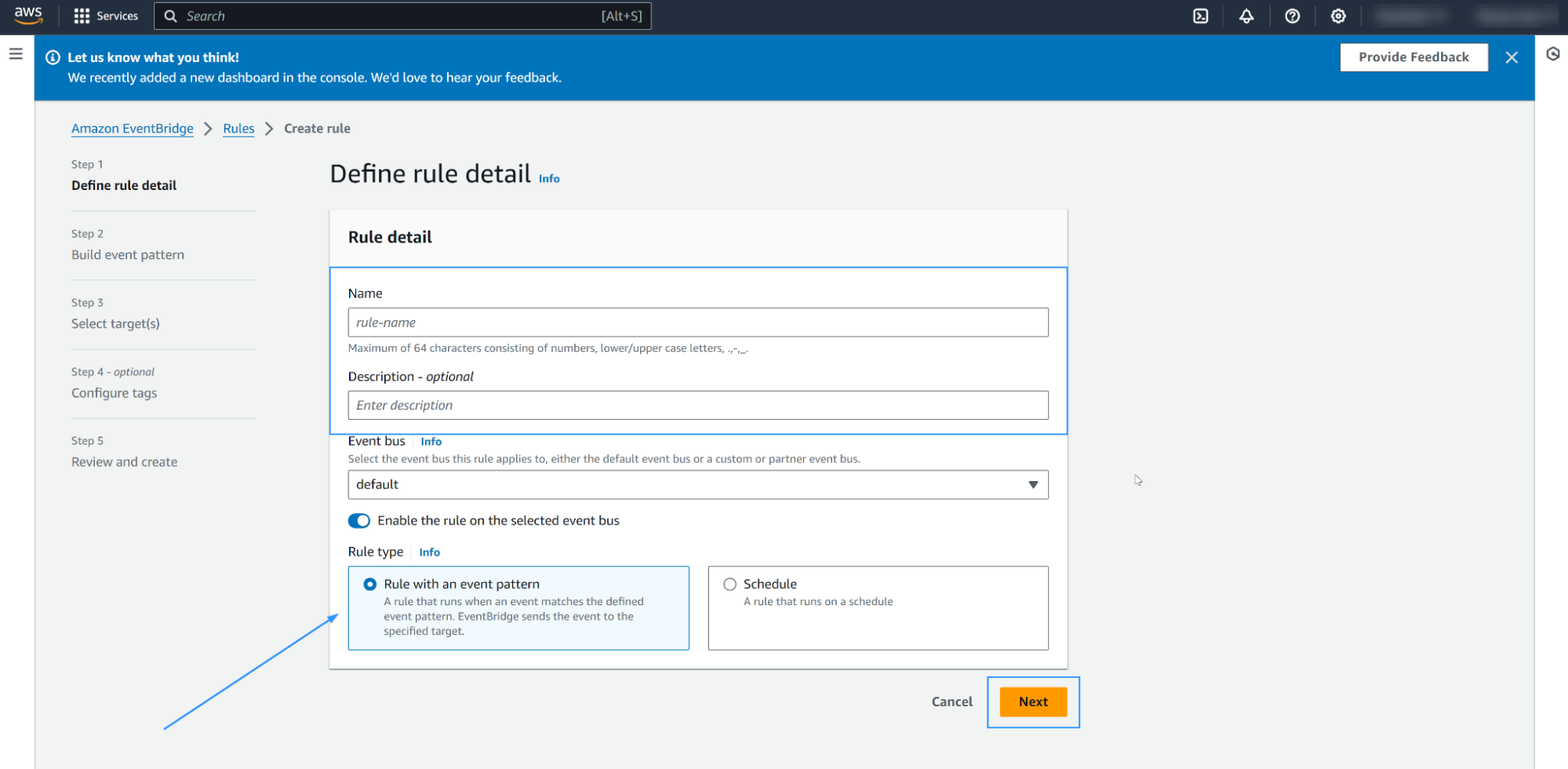
Scroll down to Event pattern. Select
Security Hubas the AWS service andAll Eventsin the Event type. Then click on Next.
Select
Firehose streamas the target, and use the Firehose stream you created in the previous section. Click on Next.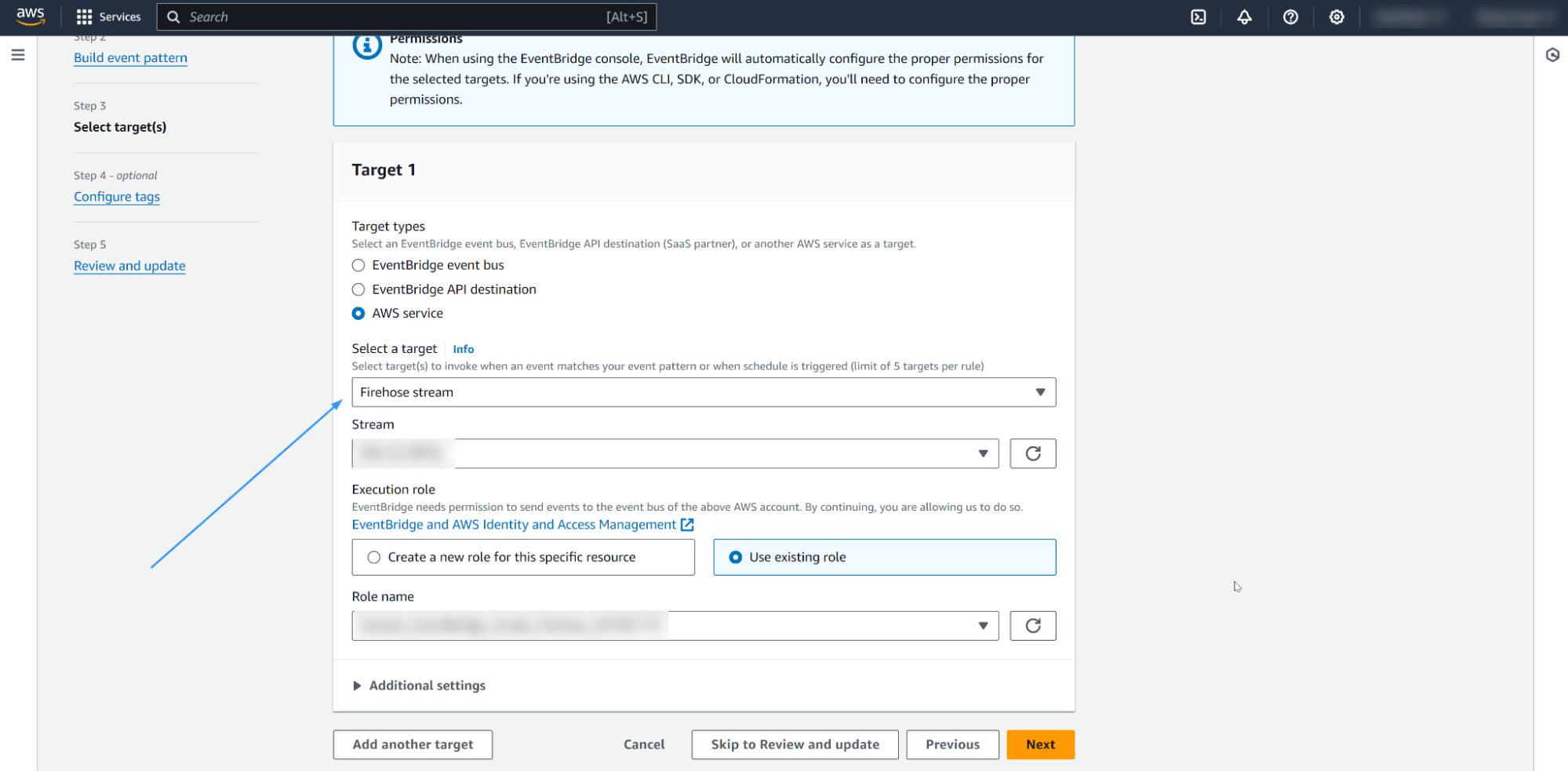
Leave the other default options and create the EventBridge rule.
The AWS documentation provides steps to configure an EventBridge rule for AWS Security Hub.
Amazon S3 bucket with event notifications
Follow the steps below to configure an S3 bucket that reports the creation of events.
Configure an S3 bucket as defined in the configuring an AWS S3 Bucket section. Provide the name you decided in the previous section.
Go to Event notifications inside the Properties tab. Select Create event notification.
Select All object create events in Event Types. This generates notifications for any event that creates an object in the bucket.
Select SQS queue in the Destination section.
Select Choose from your SQS queues. Then, choose the queue you created previously.
Amazon Simple Queue Service
Amazon Simple Queue Service is a fully managed message queuing service that makes it easy to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications.
In this case, it acknowledges new events to pull from the S3 bucket.
Set up a Standard type SQS Queue with the default configurations. You can apply an access policy similar to the following example, where
<REGION>,<AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>,<S3_BUCKET>,<YOUR_SQS_QUEUE_NAME>are your region, account ID, S3 bucket name, and SQS queue name.{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Id": "SecurityHub-ID", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "example-access-policy", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "s3.amazonaws.com" }, "Action": "SQS:SendMessage", "Resource": "arn:aws:sqs:<REGION>:<AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>:<AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>:<YOUR_SQS_QUEUE_NAME>", "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "aws:SourceAccount": "<AWS_ACCOUNT_ID>" }, "ArnLike": { "aws:SourceArn": "arn:aws:s3:*:*:<S3_BUCKET>" } } } ] }
The other settings related to this configuration are:
"Version"specifies the version of the policy language being used, in this case, the version from 2012-10-17."Id"is a unique identifier for this policy."Statement"is an array that contains the individual permission statements for this policy."Sid"is an optional identifier that provides a way to give the statement a unique name."Effect"defines whether the statement results in an"Allow"or"Deny"for the specified actions."Principal"specifies the AWS service or account allowed to access the resource, in this case, the"s3.amazonaws.com"service."Action"specifies the action that is allowed or denied, in this case, "SQS", which allows sending messages to an SQS queue."Condition"specifies conditional elements that must be met for the policy to take effect."Resource"is the ARN of your SQS queue."aws:SourceAccount"is your AWS account ID."aws:SourceArn"is the ARN of the Amazon S3 bucket created for your Amazon Security Hub logs.
You can set your access policy to accept S3 notifications from different account IDs and apply different conditions. For more information, see managing access in Amazon SQS.
Wazuh configuration
Authentication
The available authentication methods are the following:
These authentication methods require providing credentials using the /root/.aws/credentials file. For more information, see configuring AWS credentials.
Configuration
You can perform the following configuration on the Wazuh server or Linux-based Wazuh agent.
Edit the
/var/ossec/etc/ossec.conffile. Add the SQS name within the<sqs_name>tag. For example:<wodle name="aws-s3"> <disabled>no</disabled> <interval>1h</interval> <run_on_start>yes</run_on_start> <subscriber type="security_hub"> <sqs_name>YOUR_SQS_QUEUE_NAME</sqs_name> <aws_profile>YOUR_AWS_CREDENTIAL_PROFILE</aws_profile> </subscriber> </wodle>
Where:
<interval>is the time taken between each log pull.<run_on_start>pulls AWS Security Hub logs each time the Wazuh server starts.<subscriber type="security_hub">are the added tags to obtain AWS Security Hub logs.<sqs_name>is the name of the Amazon SQS queue created in the previous section.
Optional
<service_endpoint>– The AWS S3 endpoint URL for data downloading from the bucket. Check using non-default AWS endpoints for more information about VPC and FIPS endpoints.
Restart the Wazuh server or agent to apply the changes.
Wazuh server:
# systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Wazuh agent:
# Systemctl restart Wazuh-agent
Check the AWS S3 module reference to learn more about the available settings. Configure the following fields to set the queue and authentication configuration. For more information, check the subscriber’s reference.
Warning
Every message sent to the queue is read and deleted. Make sure you only use the queue for bucket notifications.
Visualizing the events
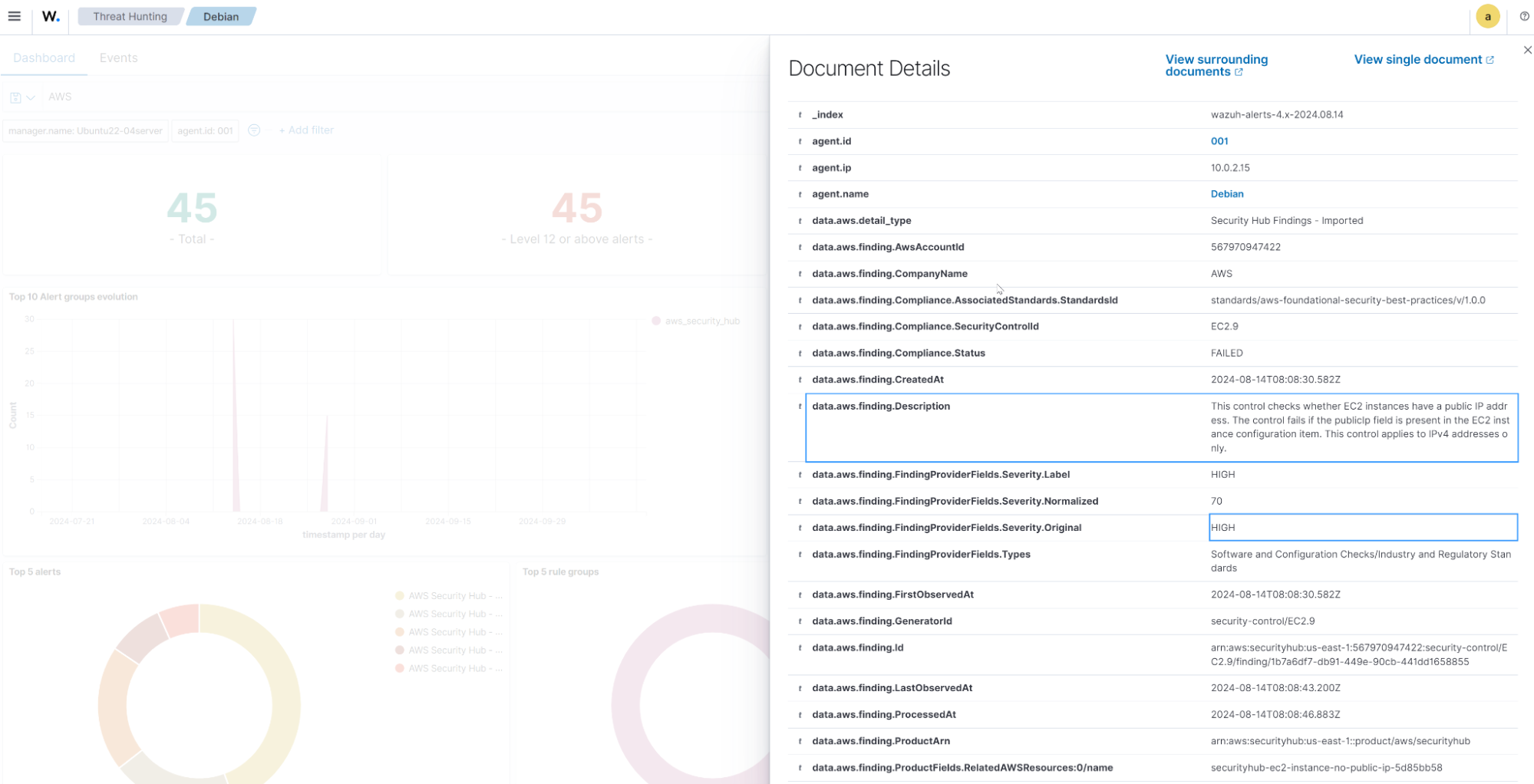
You can view these logs via the Threat Hunting dashboard of the agent you configured your Wazuh module for AWS.
The following dashboard shows the top 5 AWS Security Hub alerts discovered within 90 days.
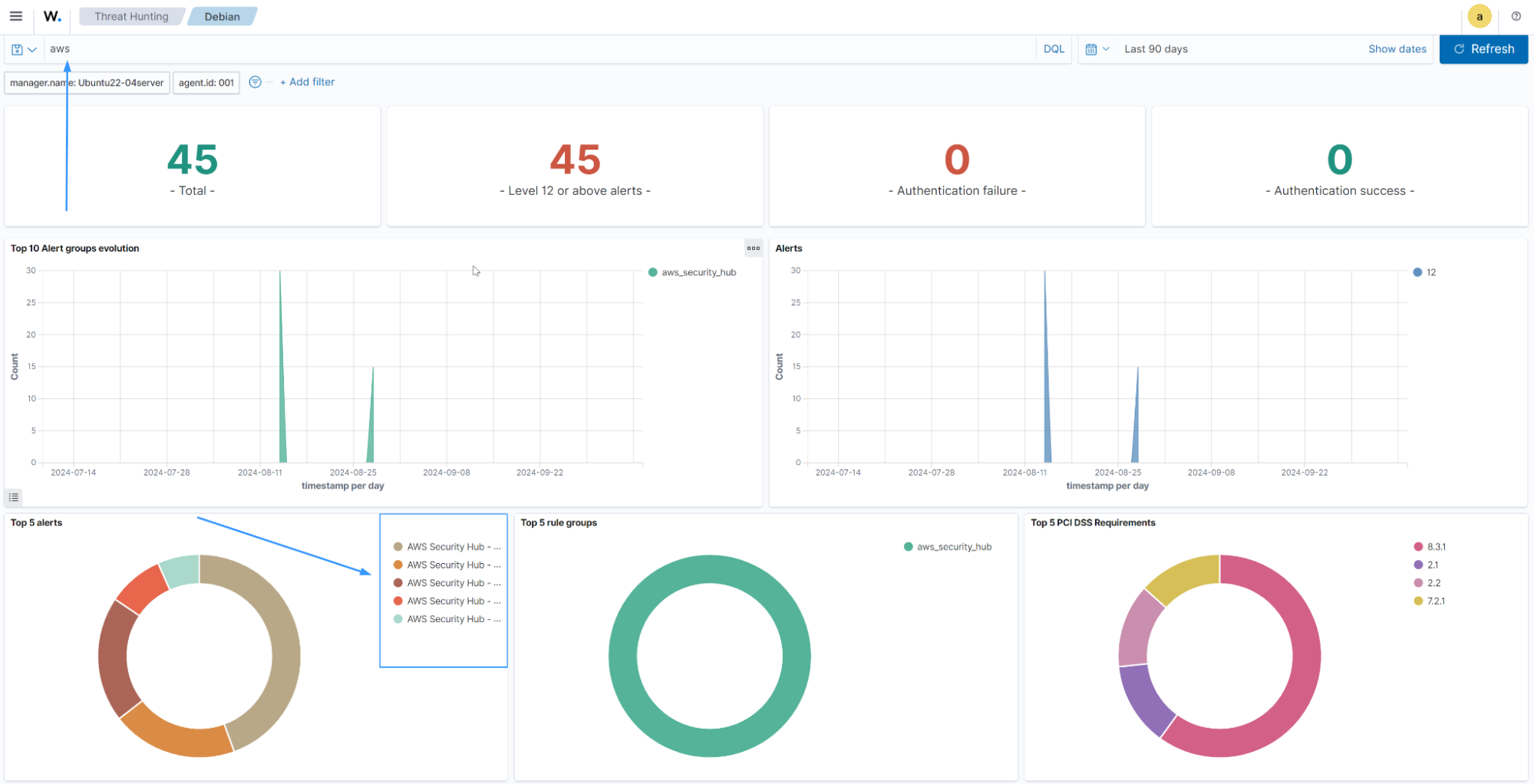
The image below shows an event with a high severity.