Load balancers
A load balancer distributes workloads across multiple resources. In this case, it distributes Wazuh agents among the different worker nodes in a Wazuh server cluster.
Wazuh recommends the following load balancers including NGINX and HAProxy. You can choose any of the load balancer services as per your need.
NGINX
NGINX is an open source web server that can also be used as a reverse proxy, load balancer, mail proxy, and HTTP cache. In this scenario, we use it as a load balancer to distribute Wazuh agent traffic within a Wazuh server cluster.
Installation
There are different installation instructions for installing NGINX based on the choice of your Linux distribution.
Download the packages from the Official page.
Follow the steps related to that guide to install the packages.
Configuration
The way NGINX and its modules work are determined in it’s configuration file. By default, the configuration file of NGINX is named nginx.conf and located in the /usr/local/nginx/conf, /etc/nginx, or /usr/local/etc/nginx directory depending on the installation type.
Perform the steps below to configure NGINX as a load balancer.
Add the content below to the NGINX
nginx.confconfiguration file:stream { upstream master { server <MASTER_NODE_IP_ADDRESS>:1515; } upstream mycluster { hash $remote_addr consistent; server <MASTER_NODE_IP_ADDRESS>:1514; server <WORKER_NODE_IP_ADDRESS>:1514; server <WORKER_NODE_IP_ADDRESS>:1514; } server { listen 1515; proxy_pass master; } server { listen 1514; proxy_pass mycluster; } }
Replace:
<MASTER_NODE_IP_ADDRESS>with the IP address of the Wazuh server master node in your cluster.<WORKER_NODE_IP_ADDRESS>with the IP address of the Wazuh server worker nodes in your cluster.
You can find more details in the NGINX guide for configuring TCP and UDP load balancer.
Verify the NGINX configuration file for syntax errors:
# nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Reload the NGINX service to apply the changes:
# nginx -s reload
HAProxy
High Availability Proxy (HAProxy) is a free and open source software that provides a high availability load balancer and proxy for TCP and HTTP-based applications. Using a load balancer, such as HAProxy, ensures the Wazuh agents enroll and report to Wazuh manager nodes in a distributed way. HAProxy supports several load balancing including round-robin, leastconn, source, and others. The load balancer assigns manager nodes to the Wazuh agents based on the selected algorithm, improving load distribution. If a Wazuh manager node fails, the Wazuh agents reconnect to another node in the cluster.
Installation
There are two main ways to install HAProxy.
Using system packages and Personal Package Archive (PPA).
Using Docker images.
Note
The provided examples and configurations are based on Ubuntu and HAProxy 2.8.
Install HAProxy
# apt install haproxy -y
Check the installation
# haproxy -v
HAProxy version 2.8.5-1ubuntu3 2024/04/01 - https://haproxy.org/ Status: long-term supported branch - will stop receiving fixes around Q2 2028. Known bugs: http://www.haproxy.org/bugs/bugs-2.8.5.html Running on: Linux 6.8.0-76060800daily20240311-generic #202403110203~1714077665~22.04~4c8e9a0 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Thu A x86_64
Add the PPA repository
# apt update && apt install software-properties-common -y # add-apt-repository ppa:vbernat/haproxy-2.8 -y
Install HAProxy
# apt install haproxy -y
Check the installation
# haproxy -v
HAProxy version 2.8.9-1ppa1~jammy 2024/04/06 - https://haproxy.org/ Status: long-term supported branch - will stop receiving fixes around Q2 2028. Known bugs: http://www.haproxy.org/bugs/bugs-2.8.9.html Running on: Linux 6.8.0-76060800daily20240311-generic #202403110203~1714077665~22.04~4c8e9a0 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Thu A x86_64
We provide the following files for installing HAProxy with Docker.
Dockerfile
FROM haproxytech/haproxy-ubuntu:2.8
COPY haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
COPY haproxy-service /etc/init.d/haproxy
COPY entrypoint.sh /entrypoint.sh
RUN chmod +x /etc/init.d/haproxy
RUN chmod +x /entrypoint.sh
ENTRYPOINT [ "/entrypoint.sh" ]
entrypoint.sh
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# Start HAProxy service
service haproxy start
tail -f /dev/null
haproxy-service
#!/bin/sh
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: haproxy
# Required-Start: $local_fs $network $remote_fs $syslog $named
# Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $syslog $named
# Default-Start: 2 3 4 5
# Default-Stop: 0 1 6
# Short-Description: fast and reliable load balancing reverse proxy
# Description: This file should be used to start and stop haproxy.
### END INIT INFO
# Author: Arnaud Cornet <acornet@debian.org>
PATH=/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/bin
BASENAME=haproxy
PIDFILE=/var/run/${BASENAME}.pid
CONFIG=/etc/${BASENAME}/${BASENAME}.cfg
HAPROXY=/usr/sbin/haproxy
RUNDIR=/run/${BASENAME}
EXTRAOPTS=
test -x $HAPROXY || exit 0
if [ -e /etc/default/${BASENAME} ]; then
. /etc/default/${BASENAME}
fi
test -f "$CONFIG" || exit 0
[ -f /etc/default/rcS ] && . /etc/default/rcS
. /lib/lsb/init-functions
check_haproxy_config()
{
$HAPROXY -c -f "$CONFIG" $EXTRAOPTS >/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 1 ]; then
log_end_msg 1
exit 1
fi
}
haproxy_start()
{
[ -d "$RUNDIR" ] || mkdir "$RUNDIR"
chown haproxy:haproxy "$RUNDIR"
chmod 2775 "$RUNDIR"
check_haproxy_config
start-stop-daemon --quiet --oknodo --start --pidfile "$PIDFILE" \
--exec $HAPROXY -- -f "$CONFIG" -D -p "$PIDFILE" \
$EXTRAOPTS || return 2
return 0
}
haproxy_stop()
{
if [ ! -f $PIDFILE ] ; then
# This is a success according to LSB
return 0
fi
ret=0
tmppid="$(mktemp)"
# HAProxy's pidfile may contain multiple PIDs, if nbproc > 1, so loop
# over each PID. Note that start-stop-daemon has a --pid option, but it
# was introduced in dpkg 1.17.6, post wheezy, so we use a temporary
# pidfile instead to ease backports.
for pid in $(cat $PIDFILE); do
echo "$pid" > "$tmppid"
start-stop-daemon --quiet --oknodo --stop \
--retry 5 --pidfile "$tmppid" --exec $HAPROXY || ret=$?
done
rm -f "$tmppid"
[ $ret -eq 0 ] && rm -f $PIDFILE
return $ret
}
haproxy_reload()
{
check_haproxy_config
$HAPROXY -f "$CONFIG" -p $PIDFILE -sf $(cat $PIDFILE) -D $EXTRAOPTS \
|| return 2
return 0
}
haproxy_status()
{
if [ ! -f $PIDFILE ] ; then
# program not running
return 3
fi
for pid in $(cat $PIDFILE) ; do
if ! ps --no-headers p "$pid" | grep haproxy > /dev/null ; then
# program running, bogus pidfile
return 1
fi
done
return 0
}
case "$1" in
start)
log_daemon_msg "Starting haproxy" "${BASENAME}"
haproxy_start
ret=$?
case "$ret" in
0)
log_end_msg 0
;;
1)
log_end_msg 1
echo "pid file '$PIDFILE' found, ${BASENAME} not started."
;;
2)
log_end_msg 1
;;
esac
exit $ret
;;
stop)
log_daemon_msg "Stopping haproxy" "${BASENAME}"
haproxy_stop
ret=$?
case "$ret" in
0|1)
log_end_msg 0
;;
2)
log_end_msg 1
;;
esac
exit $ret
;;
reload|force-reload)
log_daemon_msg "Reloading haproxy" "${BASENAME}"
haproxy_reload
ret=$?
case "$ret" in
0|1)
log_end_msg 0
;;
2)
log_end_msg 1
;;
esac
exit $ret
;;
restart)
log_daemon_msg "Restarting haproxy" "${BASENAME}"
haproxy_stop
haproxy_start
ret=$?
case "$ret" in
0)
log_end_msg 0
;;
1)
log_end_msg 1
;;
2)
log_end_msg 1
;;
esac
exit $ret
;;
status)
haproxy_status
ret=$?
case "$ret" in
0)
echo "${BASENAME} is running."
;;
1)
echo "${BASENAME} dead, but $PIDFILE exists."
;;
*)
echo "${BASENAME} not running."
;;
esac
exit $ret
;;
*)
echo "Usage: /etc/init.d/${BASENAME} {start|stop|reload|restart|status}"
exit 2
;;
esac
:
haproxy.cfg configuration file to get the service up and running.
Perform the following steps to install HAProxy with docker.
Put the files in the same directory:
Verify the files are in the same directory:
# tree . ├── Dockerfile ├── entrypoint.sh ├── haproxy.cfg └── haproxy-service
Build the image.
# docker build --tag=haproxy-deploy .
Run the HAProxy service:
# docker run haproxy-deploy
TCPLOG: true HTTPLOG: true * Starting haproxy haproxy [NOTICE] (33) : haproxy version is 2.8.9-1842fd0 [NOTICE] (33) : path to executable is /usr/sbin/haproxy [ALERT] (33) : config : parsing [/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg:3] : 'pidfile' already specified. Continuing.
Configuration
Perform the following steps to configure HAProxy to work with a Wazuh server cluster.
Create a
haproxy.cfgfile in the/etc/haproxy/directory and add the following configuration:haproxy.cfg
global chroot /var/lib/haproxy pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid maxconn 4000 user haproxy group haproxy stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats level admin log 127.0.0.1 local2 info defaults mode http maxconn 4000 log global option redispatch option dontlognull option tcplog timeout check 10s timeout connect 10s timeout client 1m timeout queue 1m timeout server 1m retries 3 frontend wazuh_register mode tcp bind :1515 default_backend wazuh_register backend wazuh_register mode tcp balance leastconn server master <IP_ADDRESS_OR_DNS_OF_WAZUH_MASTER_NODE>:1515 check server worker1 <IP_ADDRESS_OR_DNS_OF_WAZUH_WORKER_NODE>:1515 check server workern <IP_ADDRESS_OR_DNS_OF_WAZUH_WORKER_NODE>:1515 check # Do not include the following if you will enable HAProxy Helper frontend wazuh_reporting_front mode tcp bind :1514 name wazuh_reporting_front_bind default_backend wazuh_reporting backend wazuh_reporting mode tcp balance leastconn server master <IP_ADDRESS_OR_DNS_OF_WAZUH_MASTER_NODE>:1514 check server worker1 <IP_ADDRESS_OR_DNS_OF_WAZUH_WORKER_NODE>:1514 check server worker2 <IP_ADDRESS_OR_DNS_OF_WAZUH_WORKER_NODE>:1514 check
Replace:
<IP_ADDRESS_OR_DNS_OF_WAZUH_MASTER_NODE>with the IP address or DNS of the Wazuh server master node in your cluster.<IP_ADDRESS_OR_DNS_OF_WAZUH_WORKER_NODE>with the IP address or DNS of the Wazuh server worker nodes in your cluster.
The configuration above is made of the following sections defined below.
A backend section which is a set of Wazuh server cluster nodes that receive forwarded agent connections. It includes the following parameters:
The load balancing mode.
The load balance algorithm to use.
A list of Wazuh servers and ports. The example that follows has the default one pointing to the master node.
backend wazuh_register mode tcp balance leastconn server master_node <WAZUH_REGISTRY_HOST>:1515 check
A frontend section defines how to forward requests to backends. It's composed of the following parameters:
The type of load balancing.
The port to bind the connections.
The default backend to forward requests
frontend wazuh_register mode tcp bind :1515 default_backend wazuh_register
Start the service to apply the configuration:
# service haproxy start
* Starting haproxy haproxy [NOTICE] (13231) : haproxy version is 2.8.9-1ppa1~jammy [NOTICE] (13231) : path to executable is /usr/sbin/haproxy [ALERT] (13231) : config : parsing [/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg:3] : 'pidfile' already specified. Continuing.
HAProxy helper
This is an optional tool to manage HAProxy configuration depending on the Wazuh server cluster status in real time. It provides the Wazuh manager with the ability to automatically balance the Wazuh agent TCP sessions.
Key features of HAProxy helper
Some of its key features are:
Adding and removing servers to the Wazuh backend (
1514/tcp) when detecting changes on the Wazuh server cluster. For example, new workers connected.Balancing excess Wazuh agents per node when adding new servers to the Wazuh backend.
Balancing agents when detecting an imbalance that exceeds the given tolerance.
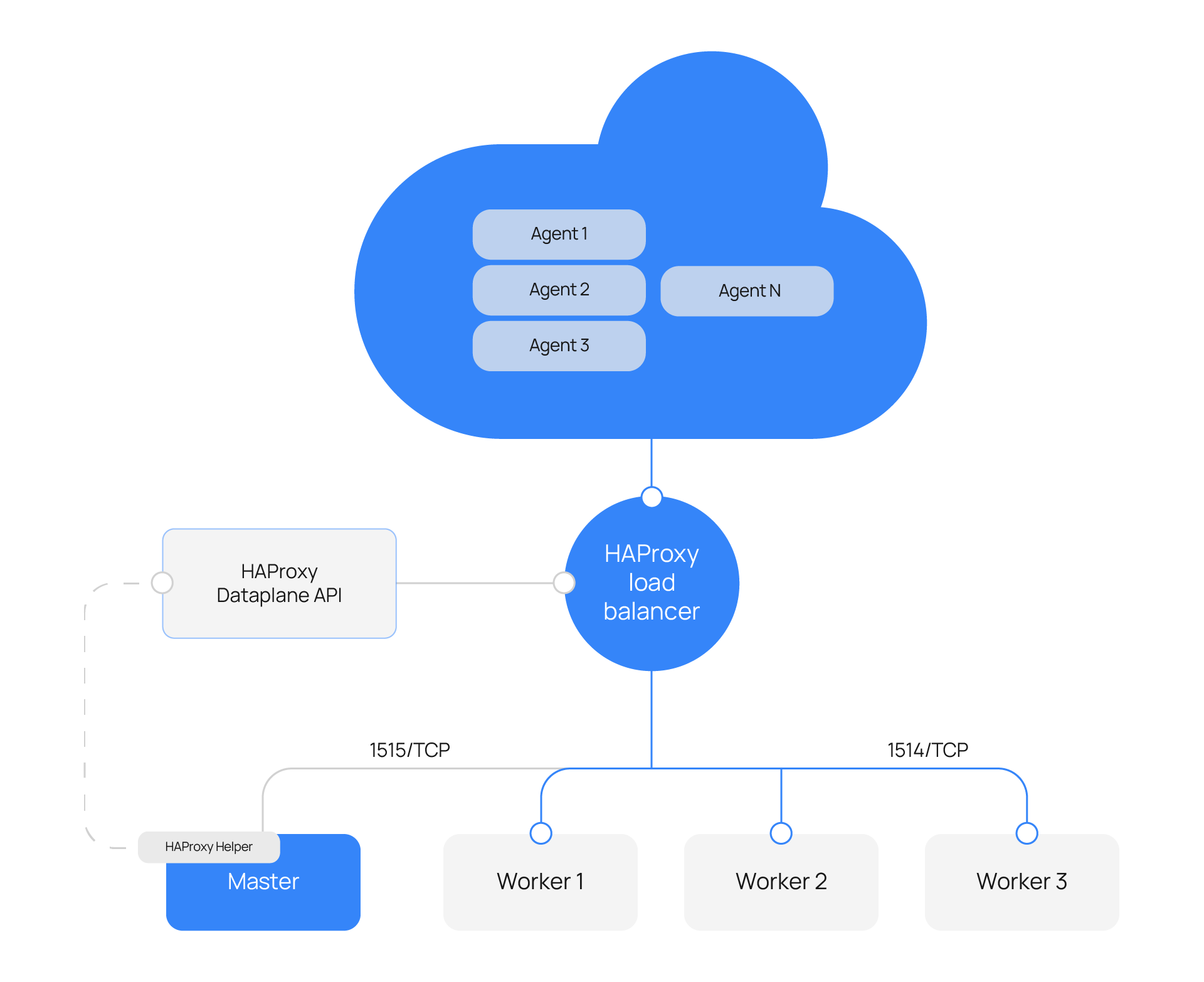
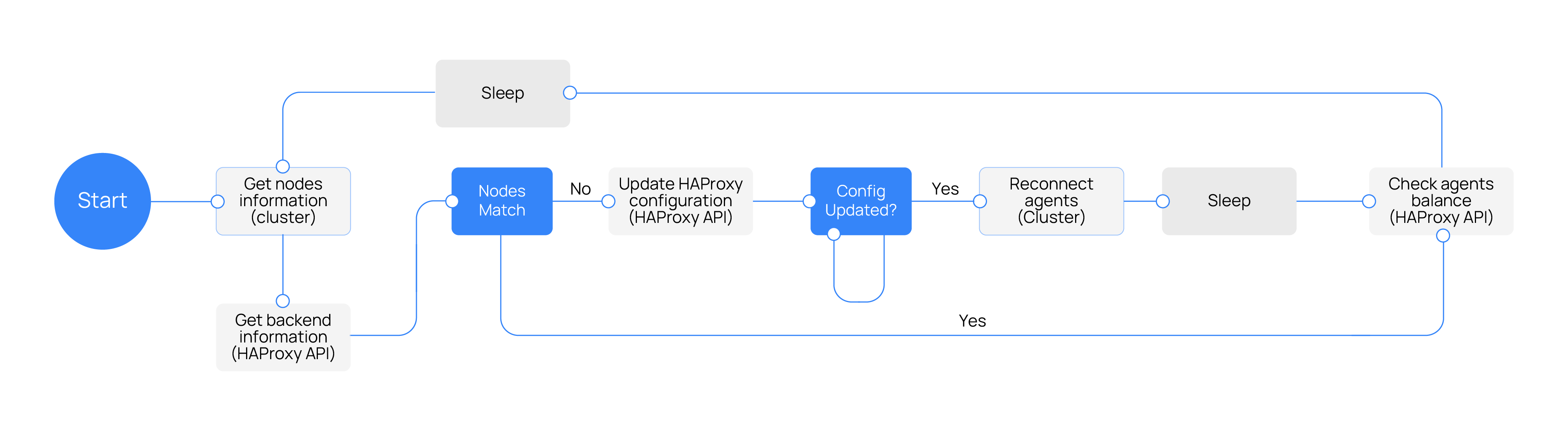
The HAProxy helper runs in an independent thread that initiates with the wazuh-cluster daemon. It follows this process.
Enabling the HAProxy helper
To use this feature, you need a HAProxy instance balancing the Wazuh server cluster using the least connections algorithm.
Note
The recommended version of HAProxy is the 2.8 LTS.
Dataplane API configuration
The HAProxy helper uses the Dataplane API to communicate with HAProxy and update the configuration according to the changes in the Wazuh server cluster.
This is the basic configuration for the Dataplane API. Replace <DATAPLANE_USER> and <DATAPLANE_PASSWORD> with the chosen user and password.
dataplaneapi:
host: 0.0.0.0
port: 5555
transaction:
transaction_dir: /tmp/haproxy
user:
- insecure: true
password: <DATAPLANE_PASSWORD>
name: <DATAPLANE_USER>
haproxy:
config_file: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
haproxy_bin: /usr/sbin/haproxy
reload:
reload_delay: 5
reload_cmd: service haproxy reload
restart_cmd: service haproxy restart
Note
If you use HTTPS as the Dataplane API communication protocol, you must set the tls field and related subfields: tls_port, tls_certificate and tls_key in the configuration. The tls_ca field is only necessary when using client-side certificates.
To generate the certificate files for both the HAProxy instance and the Wazuh server, use the following command.
# openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout <KEY_FILE_NAME> -out <CERTIFICATE_FILE_NAME> -sha256 -nodes -addext "subjectAltName=DNS:<FQDN>" -subj "/C=US/ST=CA/O=Wazuh>/CN=<CommonName>"
dataplaneapi:
scheme:
- https
host: 0.0.0.0
port: 5555
transaction:
transaction_dir: /tmp/haproxy
tls:
tls_port: 6443
tls_certificate: /etc/haproxy/ssl/<HAPROXY_CERTIFICATE_FILE>
tls_key: /etc/haproxy/ssl/<HAPROXY_CERTIFICATE_KEY_FILE>
tls_ca: /etc/haproxy/ssl/<CLIENT_SIDE_CERTIFICATE_FILE>
user:
- insecure: true
password: <DATAPLANE_PASSWORD>
name: <DATAPLANE_USER>
haproxy:
config_file: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
haproxy_bin: /usr/sbin/haproxy
reload:
reload_delay: 5
reload_cmd: service haproxy reload
restart_cmd: service haproxy restart
Depending on the HAProxy installation method, follow these steps to enable the HAProxy helper.
Warning
For the HAProxy helper to operate correctly, ensure there's no frontend with port 1514 in the haproxy.cfg file.
Download the binary file for the installed HAProxy version. You can find the available versions here.
# curl -sL https://github.com/haproxytech/dataplaneapi/releases/download/v2.8.X/dataplaneapi_2.8.X_linux_x86_64.tar.gz | tar xz && cp dataplaneapi /usr/local/bin/
Put the configuration in
/etc/haproxy/dataplaneapi.ymland start the process# dataplaneapi -f /etc/haproxy/dataplaneapi.yml &
Verify the API is running properly. Replace
<DATAPLANE_USER>and<DATAPLANE_PASSWORD>with the chosen user and password.# curl -X GET --user <DATAPLANE_USER>:<DATAPLANE_PASSWORD> http://localhost:5555/v2/info
{"api":{"build_date":"2024-05-13T12:09:33.000Z","version":"v2.8.X 13ba2b34"},"system":{}}# curl -k -X GET --user <DATAPLANE_USER>:<DATAPLANE_PASSWORD> https://localhost:6443/v2/info
{"api":{"build_date":"2024-05-13T12:09:33.000Z","version":"v2.8.X 13ba2b34"},"system":{}}
Put the configuration into
dataplaneapi.yaml# tree . ├── dataplaneapi.yml ├── Dockerfile ├── entrypoint.sh ├── haproxy.cfg └── haproxy-service
Modify
Dockerfileto includedataplaneapi.yamlduring the buildFROM haproxytech/haproxy-ubuntu:2.8 COPY haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg COPY dataplaneapi.yml /etc/haproxy/dataplaneapi.yml COPY haproxy-service /etc/init.d/haproxy COPY entrypoint.sh /entrypoint.sh RUN chmod +x /etc/init.d/haproxy RUN chmod +x /entrypoint.sh ENTRYPOINT [ "/entrypoint.sh" ]
FROM haproxytech/haproxy-ubuntu:2.8 COPY haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg COPY dataplaneapi.yml /etc/haproxy/dataplaneapi.yml COPY haproxy-service /etc/init.d/haproxy COPY entrypoint.sh /entrypoint.sh COPY <HAPROXY_CERTIFICATE_FILE> /etc/haproxy/ssl/<HAPROXY_CERTIFICATE_FILE> COPY <HAPROXY_CERTIFICATE_KEY_FILE> /etc/haproxy/ssl/<HAPROXY_CERTIFICATE_KEY_FILE> COPY <CLIENT_SIDE_CERTIFICATE_FILE> /etc/haproxy/ssl/<CLIENT_SIDE_CERTIFICATE_FILE> RUN chmod +x /etc/init.d/haproxy RUN chmod +x /entrypoint.sh ENTRYPOINT [ "/entrypoint.sh" ]
Modify the
entrypoint.shto start the dataplaneapi process#!/usr/bin/env bash # Start HAProxy service service haproxy start # Start HAProxy Data Plane API dataplaneapi -f /etc/haproxy/dataplaneapi.yml & tail -f /dev/null
Build and run the image
# docker build --tag=haproxy-deploy .
# docker run -p 5555:5555 haproxy-deploy
# docker run -p 6443:6443 haproxy-deploy
TCPLOG: true HTTPLOG: true * Starting haproxy haproxy [NOTICE] (33) : haproxy version is 2.8.9-1842fd0 [NOTICE] (33) : path to executable is /usr/sbin/haproxy [ALERT] (33) : config : parsing [/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg:3] : 'pidfile' already specified. Continuing.
Verify the API is running properly. Replace
<DATAPLANE_USER>and<DATAPLANE_PASSWORD>with the chosen user and password.# curl -X GET --user <DATAPLANE_USER>:<DATAPLANE_PASSWORD> http://localhost:5555/v2/info
# curl -k -X GET --user <DATAPLANE_USER>:<DATAPLANE_PASSWORD> https://localhost:6443/v2/info
{"api":{"build_date":"2024-05-13T14:06:03.000Z","version":"v2.9.3 59f34ea1"},"system":{}}
As an example, you can configure a basic HAProxy helper within an already configured Wazuh server cluster master node. Perform the following steps on the Wazuh server master node only.
Add the highlighted HAProxy helper configuration section to the
/var/ossec/etc/ossec.conffile:<cluster> <name>wazuh</name> <node_name>master-node</node_name> <key>c98b62a9b6169ac5f67dae55ae4a9088</key> <node_type>master</node_type> <port>1516</port> <bind_addr>0.0.0.0</bind_addr> <nodes> <node><WAZUH_MASTER_ADDRESS></node> </nodes> <hidden>no</hidden> <disabled>no</disabled> <haproxy_helper> <haproxy_disabled>no</haproxy_disabled> <haproxy_address><HAPROXY_ADDRESS></haproxy_address> <haproxy_user><DATAPLANE_USER></haproxy_user> <haproxy_password><DATAPLANE_PASSWORD></haproxy_password> </haproxy_helper> </cluster>
Where:
haproxy_disabled indicates whether the helper is disabled or not in the master node.
haproxy_address specifies the IP or DNS address to connect with HAProxy.
haproxy_user specifies the username to authenticate with HAProxy.
haproxy_password specifies the password to authenticate with HAProxy.
Learn more about haproxy_helper options in the reference guide.
<cluster> <name>wazuh</name> <node_name>master-node</node_name> <key>c98b62a9b6169ac5f67dae55ae4a9088</key> <node_type>master</node_type> <port>1516</port> <bind_addr>0.0.0.0</bind_addr> <nodes> <node><WAZUH_MASTER_ADDRESS></node> </nodes> <hidden>no</hidden> <disabled>no</disabled> <haproxy_helper> <haproxy_disabled>no</haproxy_disabled> <haproxy_address><HAPROXY_ADDRESS></haproxy_address> <haproxy_user><DATAPLANE_USER></haproxy_user> <haproxy_password><DATAPLANE_PASSWORD></haproxy_password> <haproxy_protocol>https</haproxy_protocol> <haproxy_port>6443</haproxy_port> <haproxy_cert><HAPROXY_CERTIFICATE_FILE></haproxy_cert> <client_cert><CLIENT_SIDE_CERTIFICATE_FILE></client_cert> <client_cert_key><CLIENT_SIDE_CERTIFICATE_KEY_FILE></client_cert_key> </haproxy_helper> </cluster>
Where:
haproxy_disabled indicates whether the helper is disabled or not in the master node.
haproxy_address specifies the IP or DNS address to connect with HAProxy.
haproxy_user specifies the username to authenticate with HAProxy.
haproxy_password specifies the password to authenticate with HAProxy.
haproxy_protocol specifies the protocol to use for the HAProxy Dataplane API communication. It is recommended to set it to
https.haproxy_port specifies the port used for the HAProxy Dataplane API communication.
haproxy_cert <haproxy_cert> specifies the certificate file used for the HTTPS communication. It must be the same as the one defined in the
tls_certificateparameter in thedataplaneapi.ymlfile.client_cert <client_cert> specifies the certificate file used in the client side of the HTTPS communication. It must be the same as the one defined in the
tls_caparameter in thedataplaneapi.ymlfile.client_cert_key <client_cert_key> specifies the certificate key file used in the client side of the HTTPS communication.
Learn more about haproxy_helper options in the reference guide.
Restart the Wazuh server master node:
# systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Verify the HAProxy helper is running:
# tail /var/ossec/logs/cluster.log
2024/04/05 19:23:06 DEBUG: [Cluster] [Main] Removing '/var/ossec/queue/cluster/'. 2024/04/05 19:23:06 DEBUG: [Cluster] [Main] Removed '/var/ossec/queue/cluster/'. 2024/04/05 19:23:06 INFO: [Local Server] [Main] Serving on /var/ossec/queue/cluster/c-internal.sock 2024/04/05 19:23:06 DEBUG: [Local Server] [Keep alive] Calculating. 2024/04/05 19:23:06 DEBUG: [Local Server] [Keep alive] Calculated. 2024/04/05 19:23:06 INFO: [Master] [Main] Serving on ('0.0.0.0', 1516) 2024/04/05 19:23:06 DEBUG: [Master] [Keep alive] Calculating. 2024/04/05 19:23:06 DEBUG: [Master] [Keep alive] Calculated. 2024/04/05 19:23:06 INFO: [Master] [Local integrity] Starting. 2024/04/05 19:23:06 INFO: [Master] [Local agent-groups] Sleeping 30s before starting the agent-groups task, waiting for the workers connection. 2024/04/05 19:23:06 INFO: [HAPHelper] [Main] Proxy was initialized 2024/04/05 19:23:06 INFO: [HAPHelper] [Main] Ensuring only exists one HAProxy process. Sleeping 12s before start... 2024/04/05 19:23:06 INFO: [Master] [Local integrity] Finished in 0.090s. Calculated metadata of 34 files. 2024/04/05 19:23:14 INFO: [Master] [Local integrity] Starting. 2024/04/05 19:23:14 INFO: [Master] [Local integrity] Finished in 0.005s. Calculated metadata of 34 files. 2024/04/05 19:23:18 DEBUG2: [HAPHelper] [Proxy] Obtained proxy backends 2024/04/05 19:23:18 DEBUG2: [HAPHelper] [Proxy] Obtained proxy frontends 2024/04/05 19:23:18 INFO: [HAPHelper] [Main] Starting HAProxy Helper 2024/04/05 19:23:18 DEBUG2: [HAPHelper] [Proxy] Obtained proxy servers