Leveraging LLMs for alert enrichment
Large Language Model is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) model designed to understand, generate, and manipulate human language. These models are typically built using machine learning techniques, particularly those involving deep learning and neural networks. LLMs can add human-like intelligence to process data, enhancing the efficiency of various business and personal operations. LLMs such as the ones adopted by ChatGPT have gained massive popularity and are widely used in various industries including security operations.
YARA is a tool that detects and classifies malware artifacts. While YARA can identify known patterns and signatures of malicious activity, human intervention is often required to interpret and contextualize the output of YARA scans. ChatGPT is a generative AI chatbot developed by OpenAI. It provides users with various LLMs to process data. These LLMs can analyze and enrich YARA alerts with additional context, providing security teams with deeper insights into the nature and severity of detected threats.
In this use case, we integrate Wazuh with YARA to detect when a malicious file is added to a monitored endpoint. The integration utilizes the Wazuh FIM module to monitor a directory for new or modified files. When a file modification or addition is detected, the Wazuh Active Response module triggers a YARA scan on the file. The Active Response module automatically deletes the malicious file from the endpoint if it has a positive match with a malicious signature. The Active Response module then queries ChatGPT to enrich the YARA scan result with additional insight into the malicious file that helps security teams understand its nature, potential impact, and remediation.
Infrastructure
Endpoint |
Description |
|---|---|
Ubuntu 22.04 |
Monitored endpoint configured with Wazuh File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) module and YARA integration with ChatGPT log enrichment. |
Windows 11 |
Monitored endpoint configured with Wazuh File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) module and YARA integration with ChatGPT log enrichment. |
Configuration
Perform the following steps to set up the YARA and ChatGPT integration. Choose either Ubuntu or Windows configuration depending on the operating system of the monitored endpoint.
Ubuntu 22.04 endpoint
Perform the following steps to install YARA and configure the Active Response and FIM modules.
Download, compile, and install YARA:
$ sudo apt update $ sudo apt install -y make gcc autoconf libtool libssl-dev pkg-config jq $ sudo curl -LO https://github.com/VirusTotal/yara/archive/v4.5.1.tar.gz $ sudo tar -xvzf v4.5.1.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin/ && rm -f v4.5.1.tar.gz $ cd /usr/local/bin/yara-4.5.1/ $ sudo ./bootstrap.sh && sudo ./configure && sudo make && sudo make install && sudo make check $ sudo ldconfig
Test that YARA is running properly:
$ yarayara: wrong number of arguments Usage: yara [OPTION]... [NAMESPACE:]RULES_FILE... FILE | DIR | PID Try `--help` for more options
Download YARA detection rules using valhallaAPI. Valhalla is a YARA and Sigma rule repository provided by Nextron Systems:
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/ossec/active-response/yara/rules $ sudo curl 'https://valhalla.nextron-systems.com/api/v1/get' \ -H 'Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8' \ -H 'Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.5' \ --compressed \ -H 'Referer: https://valhalla.nextron-systems.com/' \ -H 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ -H 'DNT: 1' -H 'Connection: keep-alive' -H 'Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1' \ --data 'demo=demo&apikey=1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111&format=text' \ -o /var/ossec/active-response/yara/rules/yara_rules.yar
Change the owner of the
yara_rules.yarfile toroot:wazuh, and the file permissions to750:$ sudo chown root:wazuh /var/ossec/active-response/yara/rules/yara_rules.yar $ sudo chmod 750 /var/ossec/active-response/yara/rules/yara_rules.yar
Note
If you use a custom YARA rule, ensure that the description field in the YARA rule metadata is present as this field is required to enrich the alert with ChatGPT.
Create a script
yara.shin the/var/ossec/active-response/bin/directory. This script runs YARA scans on files added or modified in the monitored directories. It also queries ChatGPT to enrich the logs and attempts to remove malware files detected by YARA.Replace
<API_KEY>with your OpenAI API key and<OPENAI_MODEL>with your preferred OpenAI model. The model used in this POC guide is gpt-4-turbo:#!/bin/bash # Wazuh - YARA active response # Copyright (C) 2015-2024, Wazuh Inc. # # This program is free software; you can redistribute it # and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public # License (version 2) as published by the FSF - Free Software # Foundation. #------------------------- Configuration -------------------------# # ChatGPT API key API_KEY="<API_KEY>" OPENAI_MODEL="<OPENAI_MODEL>" #for example gpt-4-turbo # Set LOG_FILE path LOG_FILE="logs/active-responses.log" #------------------------- Gather parameters -------------------------# # Extra arguments read INPUT_JSON YARA_PATH=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.extra_args[1]) YARA_RULES=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.extra_args[3]) FILENAME=$(echo $INPUT_JSON | jq -r .parameters.alert.syscheck.path) size=0 actual_size=$(stat -c %s ${FILENAME}) while [ ${size} -ne ${actual_size} ]; do sleep 1 size=${actual_size} actual_size=$(stat -c %s ${FILENAME}) done #----------------------- Analyze parameters -----------------------# if [[ ! $YARA_PATH ]] || [[ ! $YARA_RULES ]] then echo "wazuh-YARA: ERROR - YARA active response error. YARA path and rules parameters are mandatory." >> ${LOG_FILE} exit 1 fi #------------------------- Main workflow --------------------------# # Execute YARA scan on the specified filename YARA_output="$("${YARA_PATH}"/yara -w -r -m "$YARA_RULES" "$FILENAME")" if [[ $YARA_output != "" ]] then # Attempt to delete the file if any YARA rule matches if rm -rf "$FILENAME"; then echo "wazuh-YARA: INFO - Successfully deleted $FILENAME" >> ${LOG_FILE} else echo "wazuh-YARA: INFO - Unable to delete $FILENAME" >> ${LOG_FILE} fi # Flag to check if API key is invalid api_key_invalid=false # Iterate every detected rule while read -r line; do # Extract the description from the line using regex description=$(echo "$line" | grep -oP '(?<=description=").*?(?=")') if [[ $description != "" ]]; then # Prepare the message payload for ChatGPT payload=$(jq -n \ --arg desc "$description" \ --arg model "$OPENAI_MODEL" \ '{ model: $model, messages: [ { role: "system", content: "In one paragraph, tell me about the impact and how to mitigate \($desc)" } ], temperature: 1, max_tokens: 256, top_p: 1, frequency_penalty: 0, presence_penalty: 0 }') # Query ChatGPT for more information chatgpt_response=$(curl -s -X POST "https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" \ -d "$payload") # Check for invalid API key error if echo "$chatgpt_response" | grep -q "invalid_request_error"; then api_key_invalid=true echo "wazuh-YARA: ERROR - Invalid ChatGPT API key" >> ${LOG_FILE} # Log Yara scan result without ChatGPT response echo "wazuh-YARA: INFO - Scan result: $line | chatgpt_response: none" >> ${LOG_FILE} else # Extract the response text from ChatGPT API response response_text=$(echo "$chatgpt_response" | jq -r '.choices[0].message.content') # Check if the response text is null and handle the error if [[ $response_text == "null" ]]; then echo "wazuh-YARA: ERROR - ChatGPT API returned null response: $chatgpt_response" >> ${LOG_FILE} else # Combine the YARA scan output and ChatGPT response combined_output="wazuh-YARA: INFO - Scan result: $line | chatgpt_response: $response_text" # Append the combined output to the log file echo "$combined_output" >> ${LOG_FILE} fi fi else echo "wazuh-YARA: INFO - Scan result: $line" >> ${LOG_FILE} fi done <<< "$YARA_output" # If API key was invalid, log a specific message if $api_key_invalid; then echo "wazuh-YARA: INFO - API key is invalid. ChatGPT response omitted." >> ${LOG_FILE} fi else echo "wazuh-YARA: INFO - No YARA rule matched." >> ${LOG_FILE} fi exit 0;
Note
If the supplied
<API_KEY>is invalid, Wazuh triggers an alert with the value of thechatgpt_responsefield set toNone. Logs about the invalid API key are in the/var/ossec/logs/active-responses.logfile.Change the owner of the
yara.shscript toroot:wazuh, and the file permissions to750:$ sudo chown root:wazuh /var/ossec/active-response/bin/yara.sh $ sudo chmod 750 /var/ossec/active-response/bin/yara.sh
Add the following within the
<syscheck>block of the Wazuh agent/var/ossec/etc/ossec.confconfiguration file to monitor the/homedirectory:<directories realtime="yes">/home</directories>
Restart the Wazuh agent to apply the configuration changes:
$ sudo systemctl restart wazuh-agent
Windows 11 endpoint
Perform the following steps to install Python, YARA, and download YARA rules.
Download the Python executable installer from the official Python website.
Run the Python installer once downloaded, and make sure to check the following boxes:
Install launcher for all usersAdd python.exe to PATH. This places the Python interpreter in the execution path.
Download and install the latest Visual C++ Redistributable package.
Open PowerShell with administrator privileges to download and extract YARA:
> Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://github.com/VirusTotal/yara/releases/download/v4.5.1/yara-v4.5.1-2298-win64.zip -OutFile yara-v4.5.1-2298-win64.zip > Expand-Archive yara-v4.5.1-2298-win64.zip; Remove-Item yara-v4.5.1-2298-win64.zip
Create a directory called
C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\and copy the YARA executable into it:> mkdir 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\' > cp .\yara-v4.5.1-2298-win64\yara64.exe 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\'
Download YARA rules using valhallaAPI. Valhalla is a YARA and Sigma rule repository provided by Nextron Systems:
> python -m pip install valhallaAPI > python -c "from valhallaAPI.valhalla import ValhallaAPI; v = ValhallaAPI(api_key='1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111'); response = v.get_rules_text(); open('yara_rules.yar', 'w').write(response)" > mkdir 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\' > cp yara_rules.yar 'C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\'
Note
If you use a custom YARA rule, ensure that the description field in the YARA rule metadata is present, as this field is required to enrich the alert with ChatGPT.
Create a script
yara.pyin theC:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\directory. This script runs a YARA scan against any file modified or added to the monitored directory. It also queries ChatGPT to enrich the logs and attempts to remove malware files detected by YARA. Replace<API_KEY>with your OpenAI API key and<OPENAI_MODEL>with your preferred OpenAI model. The model used in this POC guide is gpt-4-turbo:import os import subprocess import json import re import requests API_KEY = '<API_KEY>' OPENAI_MODEL='<OPENAI_MODEL>' #for example gpt-4-turbo # Determine OS architecture and set log file path if os.environ['PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE'].endswith('86'): log_file_path = os.path.join(os.environ['ProgramFiles'], 'ossec-agent', 'active-response', 'active-responses.log') else: log_file_path = os.path.join(os.environ['ProgramFiles(x86)'], 'ossec-agent', 'active-response', 'active-responses.log') def log_message(message): with open(log_file_path, 'a') as log_file: log_file.write(message + '\n') def read_input(): return input() def get_syscheck_file_path(json_file_path): with open(json_file_path, 'r') as json_file: data = json.load(json_file) return data['parameters']['alert']['syscheck']['path'] def run_yara_scan(yara_exe_path, yara_rules_path, syscheck_file_path): try: result = subprocess.run([yara_exe_path, '-m', yara_rules_path, syscheck_file_path], capture_output=True, text=True) return result.stdout.strip() except Exception as e: log_message(f"Error running Yara scan: {str(e)}") return None def extract_description(yara_output): match = re.search(r'description="([^"]+)"', yara_output) if match: return match.group(1) else: return None def query_chatgpt(description): headers = { 'Authorization': f'Bearer {API_KEY}', 'Content-Type': 'application/json' } data = { 'model': OPENAI_MODEL, 'messages': [{'role': 'system', 'content': f'In one paragraph, tell me about the impact and how to mitigate {description}'}], 'temperature': 1, 'max_tokens': 256, 'top_p': 1, 'frequency_penalty': 0, 'presence_penalty': 0 } response = requests.post('https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions', headers=headers, json=data) if response.status_code == 200: return response.json()['choices'][0]['message']['content'] elif response.status_code == 401: # Unauthorized (invalid API key) log_message("wazuh-YARA: ERROR - Invalid ChatGPT API key") return None else: log_message(f"Error querying ChatGPT: {response.status_code} {response.text}") return None def main(): json_file_path = r"C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\stdin.txt" yara_exe_path = r"C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\yara64.exe" yara_rules_path = r"C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara\rules\yara_rules.yar" input_data = read_input() with open(json_file_path, 'w') as json_file: json_file.write(input_data) syscheck_file_path = get_syscheck_file_path(json_file_path) yara_output = run_yara_scan(yara_exe_path, yara_rules_path, syscheck_file_path) if yara_output is not None: description = extract_description(yara_output) if description: chatgpt_response = query_chatgpt(description) if chatgpt_response: combined_output = f"wazuh-YARA: INFO - Scan result: {yara_output} | chatgpt_response: {chatgpt_response}" log_message(combined_output) else: # Log the Yara scan result without the ChatGPT response log_message(f"wazuh-YARA: INFO - Scan result: {yara_output} | chatgpt_response: None") # Delete the scanned file if a description is found try: os.remove(syscheck_file_path) if not os.path.exists(syscheck_file_path): log_message(f"wazuh-YARA: INFO - Successfully deleted {syscheck_file_path}") else: log_message(f"wazuh-YARA: INFO - Unable to delete {syscheck_file_path}") except Exception as e: log_message(f"Error deleting file: {str(e)}") else: log_message("Failed to extract description from Yara output.") else: log_message("Yara scan returned no output.") if __name__ == "__main__": main()
Note
If the supplied
<API_KEY>is invalid, Wazuh triggers an alert with the value of thechatgpt_responsefield set toNone. You can find logs about the invalid API key in theC:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\active-response.logfile.Run the following command using PowerShell to convert the
yara.pyscript to an executable file:> pip install pyinstaller > pyinstaller -F "C:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\yara.py"
This creates a
yara.exeexecutable in theC:\Users\<USER>\dist\directory.Note
If you run the above commands as Administrator, the executable file will be in the
C:\Windows\System32\distdirectory.Copy the
yara.exeexecutable file toC:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\active-response\bin\directory on the monitored endpoint.Add the following within the
<syscheck>block of the Wazuh agentC:\Program Files (x86)\ossec-agent\ossec.confconfiguration file to monitor the Users directory:<directories realtime="yes">C:\Users\*\Downloads</directories>
Restart the Wazuh agent to apply the configuration changes:
> Restart-Service -Name wazuh
Wazuh server
Perform the following steps on the Wazuh server to configure custom rules, decoders, and the Active Response module.
Add the following decoders to the Wazuh server
/var/ossec/etc/decoders/local_decoder.xmlfile to parse the data in YARA scan results:<!-- YARA Decoder --> <decoder name="YARA_decoder"> <prematch>wazuh-YARA:</prematch> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">wazuh-YARA: (\S+)</regex> <order>YARA.log_type</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">Scan result: (\S+)\s+</regex> <order>YARA.rule_name</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">\[description="([^"]+)",</regex> <order>YARA.rule_description</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">author="([^"]+)",</regex> <order>YARA.rule_author</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">reference="([^"]+)",</regex> <order>YARA.reference</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">date="([^"]+)",</regex> <order>YARA.published_date</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">score =(\d+),</regex> <order>YARA.threat_score</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">customer="([^"]+)",</regex> <order>YARA.api_customer</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">hash1="([^"]+)",</regex> <order>YARA.file_hash</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">tags="([^"]+)",</regex> <order>YARA.tags</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">minimum_YARA="([^"]+)"\]</regex> <order>YARA.minimum_YARA_version</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">\] (.*) \|</regex> <order>YARA.scanned_file</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">chatgpt_response: (.*)</regex> <order>YARA.chatgpt_response</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">Successfully deleted (.*)</regex> <order>YARA.file_deleted</order> </decoder> <decoder name="YARA_child"> <parent>YARA_decoder</parent> <regex type="pcre2">Unable to delete (.*)</regex> <order>YARA.file_not_deleted</order> </decoder>
Add the following rules to the
/var/ossec/etc/rules/local_rules.xmlfile. The rules detect FIM events in the monitored directory. This triggers the YARA Active response script to delete a file if identified as a malicious file.<group name="syscheck,"> <rule id="100300" level="5"> <if_sid>550</if_sid> <field name="file">/home</field> <description>File modified in /home directory.</description> </rule> <rule id="100301" level="5"> <if_sid>554</if_sid> <field name="file">/home</field> <description>File added to /home directory.</description> </rule> <rule id="100302" level="5"> <if_sid>550</if_sid> <field name="file" type="pcre2">(?i)C:\\Users.+Downloads</field> <description>File modified in the downloads directory.</description> </rule> <rule id="100303" level="5"> <if_sid>554</if_sid> <field name="file" type="pcre2">(?i)C:\\Users.+Downloads</field> <description>File added to the downloads directory.</description> </rule> </group> <group name="yara,"> <rule id="108000" level="0"> <decoded_as>YARA_decoder</decoded_as> <description>YARA grouping rule</description> </rule> <rule id="108001" level="10"> <if_sid>108000</if_sid> <match>wazuh-YARA: INFO - Scan result: </match> <description>File "$(YARA.scanned_file)" is a positive match for YARA rule: $(YARA.rule_name)</description> </rule> <rule id="108002" level="5"> <if_sid>108000</if_sid> <field name="yara.file_deleted">\.</field> <description>Active response successfully removed malicious file "$(YARA.file_deleted)"</description> </rule> <rule id="108003" level="12"> <if_sid>108000</if_sid> <field name="YARA.file_not_deleted">\.</field> <description>Active response unable to delete malicious file "$(YARA.file_not_deleted)"</description> </rule> </group>
Add the following configuration to the Wazuh server
/var/ossec/etc/ossec.confconfiguration file. This configures the Active Response module to trigger after the rules with ID100300,100301,100302, and100303are fired:<ossec_config> <command> <name>yara_windows</name> <executable>yara.exe</executable> <timeout_allowed>no</timeout_allowed> </command> <command> <name>yara_linux</name> <executable>yara.sh</executable> <extra_args>-yara_path /usr/local/bin -yara_rules /var/ossec/active-response/yara/rules/yara_rules.yar</extra_args> <timeout_allowed>no</timeout_allowed> </command> <active-response> <disabled>no</disabled> <command>yara_linux</command> <location>local</location> <rules_id>100300,100301</rules_id> </active-response> <active-response> <disabled>no</disabled> <command>yara_windows</command> <location>local</location> <rules_id>100302,100303</rules_id> </active-response> </ossec_config>
Restart the Wazuh manager to apply the configuration changes:
$ sudo systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Testing the configuration
Ubuntu 22.04 endpoint
Run the following commands on the Ubuntu endpoint to download malware samples to the monitored /home directory:
# curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh-documentation/refs/heads/4.14/resources/samples/mirai" > /home/mirai
# curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh-documentation/refs/heads/4.14/resources/samples/xbash" > /home/xbash
# curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh-documentation/refs/heads/4.14/resources/samples/webshell" > /home/webshell
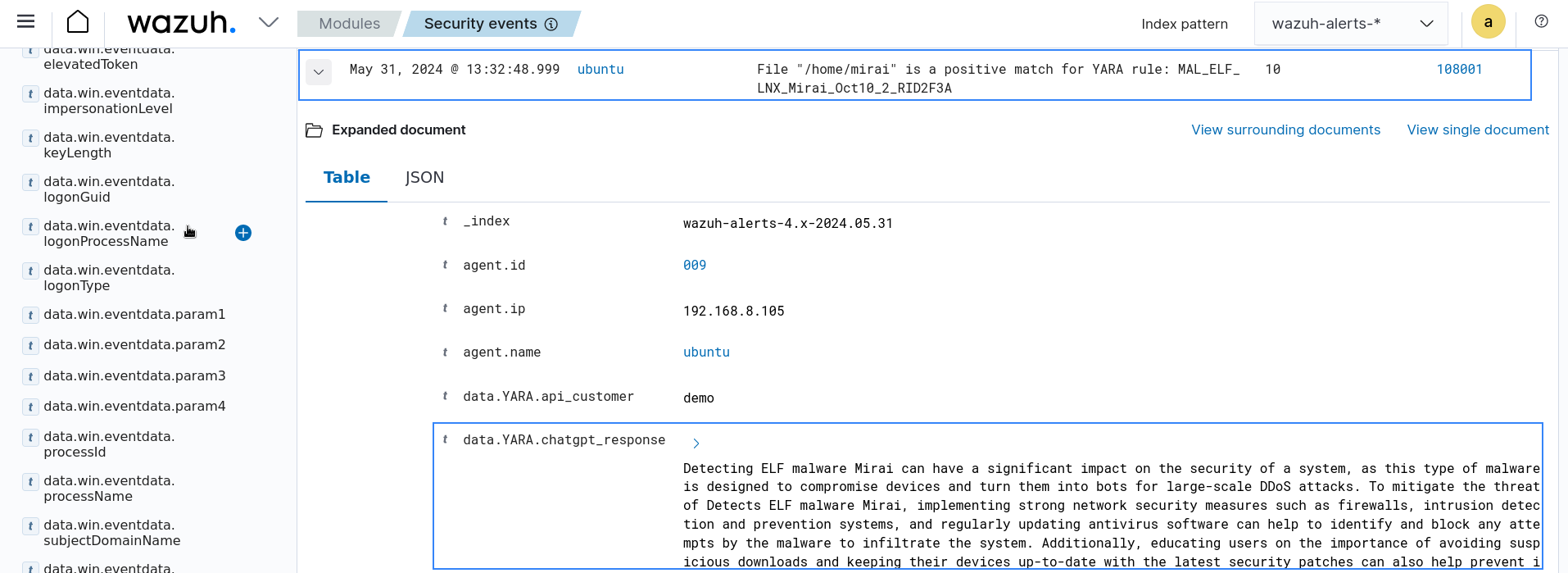
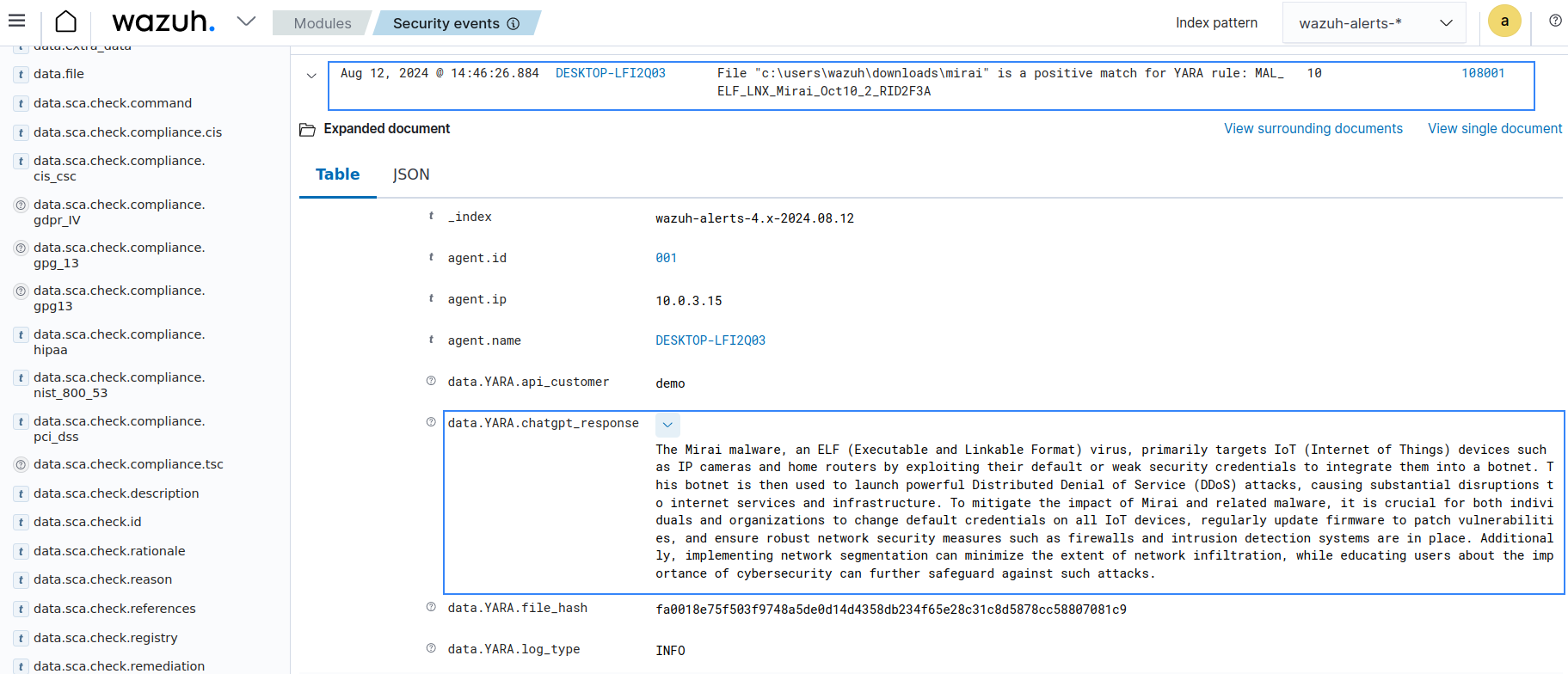
You can visualize the alert data in the Wazuh dashboard. To do this, go to the Modules > Security events tab and add the rule.groups:yara filter in the search bar to query the alerts.
As seen in the image, ChatGPT provides more context to the malicious file detected by YARA. Further insight such as origin, attack vectors, and impact of the malicious file can be seen in the yara.chatgpt_response field.
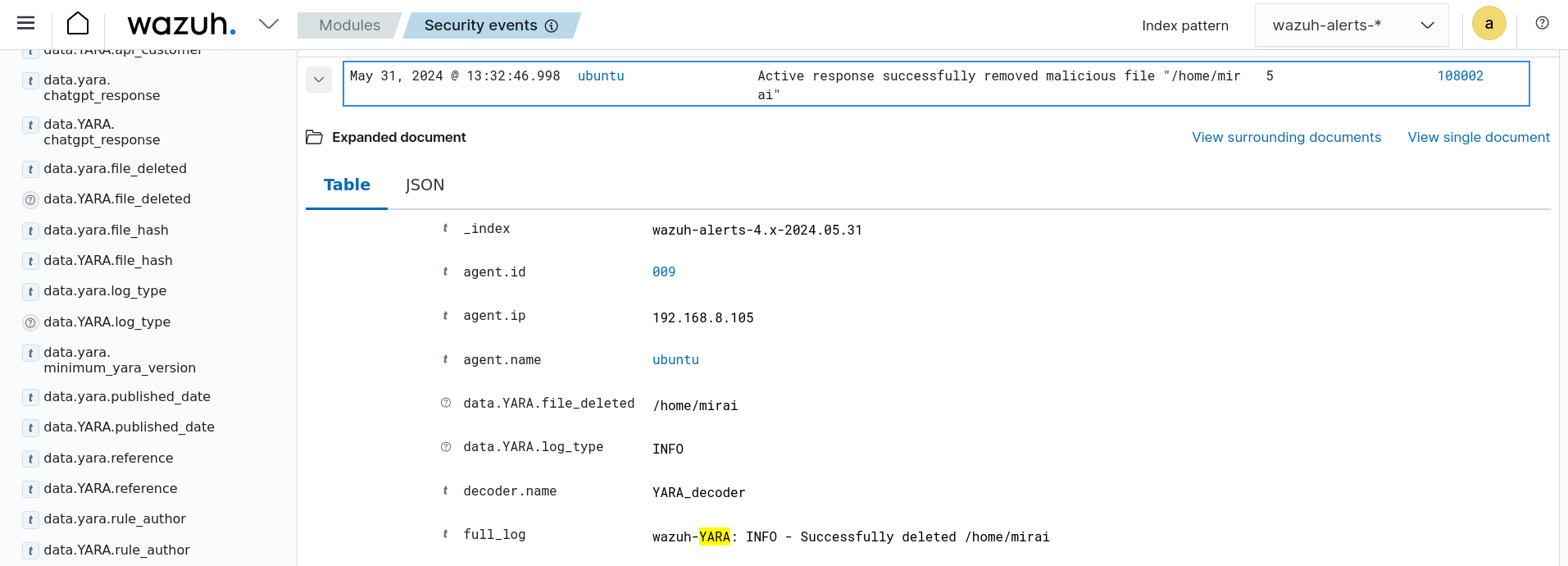
The below image shows an example of an alert triggered when the provided ChatGPT API key is invalid or a matched YARA rule does not contain a description.
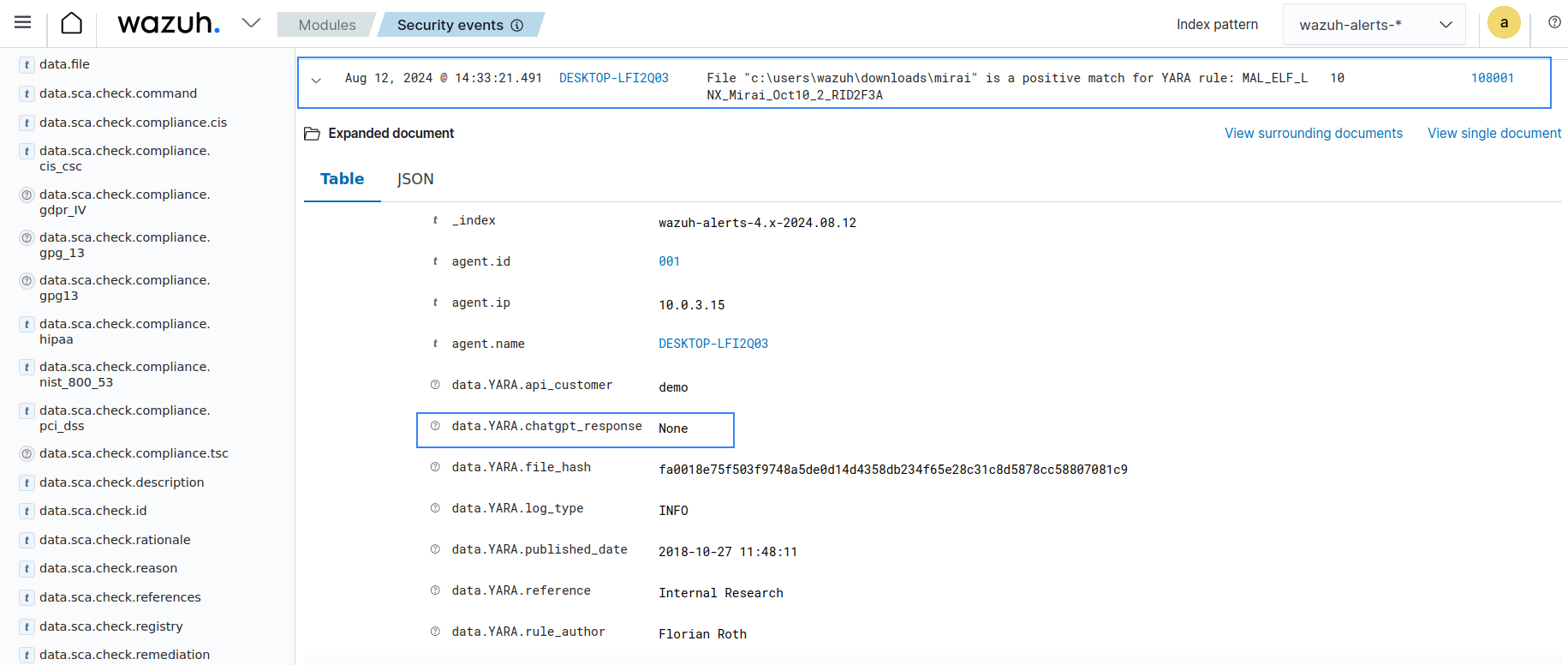
Windows 11 endpoint
Run the following commands via PowerShell to download malware samples to the monitored C:\Users\*\Downloads directory:
> curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh-documentation/refs/heads/4.14/resources/samples/mirai" -o $env:USERPROFILE\Downloads\mirai
> curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh-documentation/refs/heads/4.14/resources/samples/xbash" -o $env:USERPROFILE\Downloads\xbash
> curl "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh-documentation/refs/heads/4.14/resources/samples/webshell" -o $env:USERPROFILE\Downloads\webshell
You can visualize the alert data in the Wazuh dashboard. To do this, go to the Security events module and add the filter in the search bar to query the alerts.
rule.groups:yara
As seen in the image, ChatGPT provides more context to the malicious file detected by YARA. Further insight, such as origin, attack vectors, and impact of the malicious file, can be seen in the yara.chatgpt_response field.
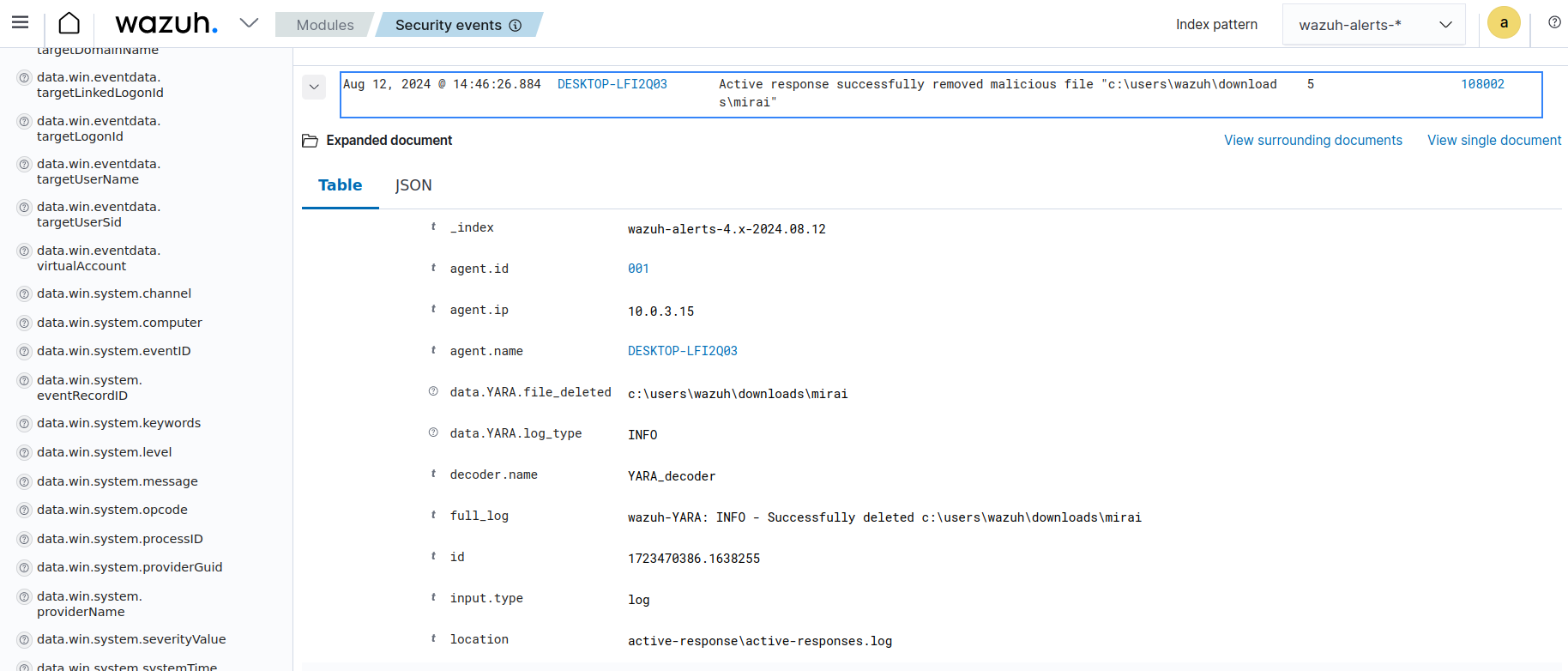
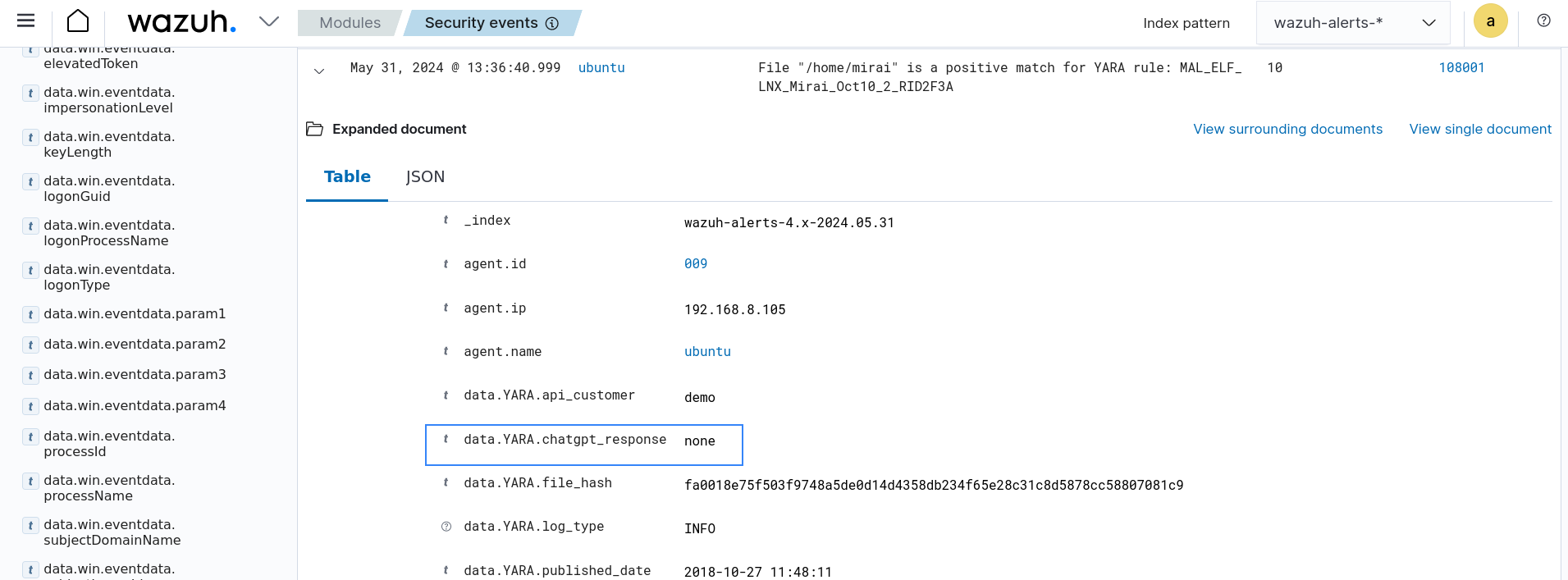
The below image shows an example of an alert triggered when the provided ChatGPT API key is invalid or a matched YARA rule does not contain a description.